You’re a radiologist staring at a CT scan, racing against time to sketch the exact borders of a lung tumor before radiation therapy. One shaky line, one oversight—could mean missing cancer cells or frying healthy tissue. It’s a real mess. And you’re thinking… “There’s gotta be a smarter way.” Surprise, surprise—there is. Tumor segmentation AI promises to match human precision while saving hours of work. But hold up. Before we throw a party for our robot overlords, let’s chat about the good, the bad, and the blurry lines.
Short on time? Here’s your cheat sheet: AI can now spot and outline tumors as clearly as experts do, especially for radiation therapy precision. Tools like Northwestern’s iSeg even account for lung tumors moving as you breathe. But can we fully let go of the pen without tripping over a landmine? Nope. Let’s dig into how this tech works—and why cancer treatment AI isn’t a “set and forget” party trick.
What’s AI Segmentation?
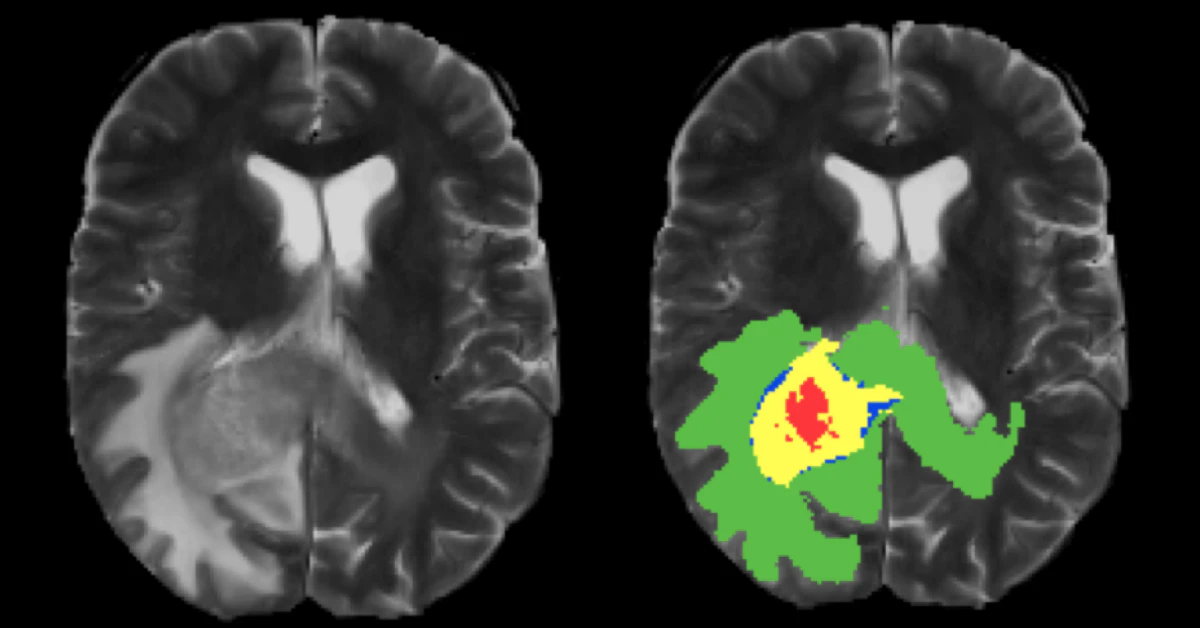
Imagine asking your phone’s camera to outline a rogue mole on your skin. Now scale that to 3D medical scans where mistakes aren’t just embarrassing—they’re dangerous. Tumor segmentation AI uses algorithms like U-Net (yep, the party starter for brain tumor mapping) to parse images pixel by pixel. Instead of a human nomming over thousands of slices, the AI zooms through datasets like BraTS2020, learning what healthy and cancerous tissue look like.
But how good is it? Check this: At Northwestern, researchers built iSeg, a platform that doesn’t just freeze-frame tumors—it tracks them in real-time. Like a michelleard. Whoa. Unlike old-school AI, it’s not just playing with static images. It’s watching tumors wiggle as you inhale, making Planning radiation a tighter dance. One doctor described it as “finally feeling like my team leveled up.”
Still, some skeptics (yep, most of them GOOD ones) say it’s like teaching a dog to tell Van Gogh from Monet. The speed? Impressive. The detail? Sometimes misses the subtleties. You’ll see why in a sec.
How AI Beats Old-School Methods
Let’s talk about how manual tumor segmentation—yes, the old “draw boundaries by hand” approach—was dragging us down. Here’s the thing:
- It takes >4 hours for complex lung tumor mapping,
- Two doctors could draw wildly different zones on the same scan,
- And fatigue? Holy stress. Even with naps, skipping a hotspot was way too easy.
Tumor segmentation AI cuts through the noise. iSeg? Turns a marathon into a mile. From ScienceDirect’s 2024 review, dynamic AI doesn’t just auto-select tissue; it watches tumors move. Think of it as giving GPS to a surgeon tracking shifting targets. “It’s like having a teammate that remembers every crumb in the cookie jar,” said Dr. Toniucci, an oncologist who tested iSeg in early trials.
But it’s not all roses. Take NVIDIA’s 3D brain tumor tracker: under perfect conditions, flawless. But throw in an odd tumor—say, all blobby or nestled by a tricky blood vessel—and it might flake. “Sometimes AI paints outside the lines,” another radiologist told me. “Which is… not okay.”
U-Net to the Rescue
If you’ve heard of AI for tumors, you’ve heard “U-Net.” Quick confession: I had no idea what this even was until today’s deep dive. Here’s the tea: U-Net is a model that eats images like a hungry beaver and spits out precise outlines. Thanks to OVHcloud’s tutorials, anyone with enough data can train their own for breast cancer or lung tumor analysis.
In GitHub land, folks are botching U-Net models in real-time. The catch? Training requires clean data. Like teaching your toddler spoon-feeding with perfect ice cream scoops—not the half-melted tragedies that happen daily. One GitHub dev wrote: “First CNN try? Total train wreck. Third? Fingers crossed it at least notices the tumor.”
Your Patient’s Breath, AI’s Beat
Side note—doctors once had to guess tumor motion during treatments (yeesh). Now, AI like iSeg syncs to breathing patterns, adjusting radiation angles on the fly. In a June 2025 study from Northwestern, tumors shifted up to 2.4 cm as lungs inflate—very real. Manual methods pretented this didn’t exist until it was morning headlines. AI’s 3D brain? Never blinks. Just tracks the bounce. According to trial docs, tumor dialing accuracy jumped 18% with deep learning tools.
Is It Future-Proof? Or Just a Fancy Toy?
Alright, racism keeps AI hungry for real-world variety. Like asking humans to guess what a kiwi is without seeing one. If the model rains on the same data well, it falters when tumors twist or pop up in underserved groups. From ScienceDirect’s 2025 reasons, hidden biases do clog brain tumor segmentation. No joke.
A pediatric imaging project at Yale hit the wall: their AI, trained on adult datasets, tagged a toddler’s tumor as “probably normal tissue.” Scary, right? They fixed it by adding diverse scans, but the moral? Algorithm or not, context is king. Semi-supervised tools like TumorPrism3D now exist to bridge gaps, but it’s all a work in progress.
When the Machine Sneezes
You may be thinking, “What if AI goes full Maverick?” While AI charges through segmentation fast, sometimes it misses strokes no human would. One radiologist described a case where an AI skipped a dime-sized lesion nestled near lung vessels. “It’s like saying, ‘Sauce in the mouth, sauce on the shirt,’ unless you’ve got quality checks.” Remote validation layers (like having a senior doc spot-check AI output) are still a must.
The Human Touch in a Digital Age
Here’s the thing: Docs adore tech, but they ain’t sleeping when algorithms get control. A 2025 partnership at Rice spun BRAINNET—a system that does AI and human workflow. Idea: docs iron out fine details while AI handles brain fatigue from liver lesions. Efficiency without the roll-the-dice approach. According to the head engineer, “it’s not replacement; it’s acceleration.”
Ahead of the Curve: Beyond Blazing Scans
In the past, tumor detection was painstaking, especially for dynamic scans. New methods like Synopsys’s AI Simpleware chugged through 3D renderings, but each scan required, like, minutes of waiting. Now? Real-time feedback from Swiss teams and NVIDIA makes your todo list shorter. And lower error rates? All kinds of gold.
Radiomics (fancy term for spatial tumor patterns) lapped up AI input from ScienceDirect’s 2024 innovations. Imagine isolating a tumor’s shape down to its texture and color shifts in MRI. That’s what the latest models are for—instant, intuitive, and scalable. But still require real people to OK the summaries.
Eyes Wide Open in Pediatric Oncology
Kids’ tumors? Wildly different from adults’. PMC’s 2022 data lit up this need with a pocketbook of tricky anatomy. Transfer learning, where AI “borrows” knowledge from adult datasets, is the hack du jour. Even with just 20 pediatric scans, they got 75% precision on tricky spots—still not gold standard, but a start.
Final Verdict: Partner or Pacifier?
So… is tumor segmentation AI a boon or just buzz? From 2025’s trials, it’s a beam of light. Tools like iSeg and TumorPrism3D let docs hit tumors dead-center, without burning happy cells. However, humans still pick up slack where AI falters.
Here’s how doctors are playing it safe:
| Strategy | Why It Counts |
|---|---|
| Multi-reader validation | Teams double-check AI-drawn borders |
| Manual edit windows | Allows doctors to tweak slices AI trips on |
| Inter-hospital trials | Tests AI on diverse populations (avoids homogeneity) |
Bottom line? If you’re curious where cancer treatment AI is headed, it’s like watching a self-driving car navigate traffic. Fast, sharp—yet still needing your hands nearby. There’s gold in those algorithms, but only if we demand more from datasets and keep humans looking.
Sounds intense? It is. But maybe that’s the point. Your role—whether you’re a doctor reading this circa late 2025 or a patient wondering how far we’ve come—is to push the system to serve you. So next time you scroll a CT scan, ask: What if the AI missed the plot twist?
So What Now?
The path ahead for AI in radiation therapy isn’t about letting go—it’s about syncing. From Switzerland’s self-segmenting MRIs to Rice’s BRAINNET, the goal’s the same: make radiation work better without cutting corners.
Don’t know a U-Net from a BD Bag? Doesn’t matter. What counts is how AI’s evolving to catch nuance—like swinging between “gtfo” and “hold on” steps. A system’s only as helpful as its understanding of complex needs, right?
If you’re wondering how to approach this wave of cancer treatment AI, let’s keep it real: lean on it, but love it like a dog—train, question, and treat it kindly. Got thoughts? Wild guesses? Fire away. Every toolhouse needs a toolbox, and the human mind’s still the master code.

















Leave a Reply
You must be logged in to post a comment.