What is lactic acid?
Lactic acid is an anti-wrinkle and pigmentation-targeting compound found in both over-the-counter (OTC) and professional skin care formulations.
Sourced from milk, lactic acid is a member of the alpha-hydroxy acid (AHA) family of anti-aging actives. Other AHAs include glycolic acid and citric acid.
Continue reading to discover how a lactic acid peel can enhance your skin, OTC products to consider, what to anticipate from a clinical peel, and more.
How can a lactic acid peel benefit your skin?
A chemical peel works by applying a chemical — in this instance, lactic acid — to cleansed skin. It strips away the outermost skin layer (epidermis). Stronger formulations can penetrate into the mid skin layers (dermis).
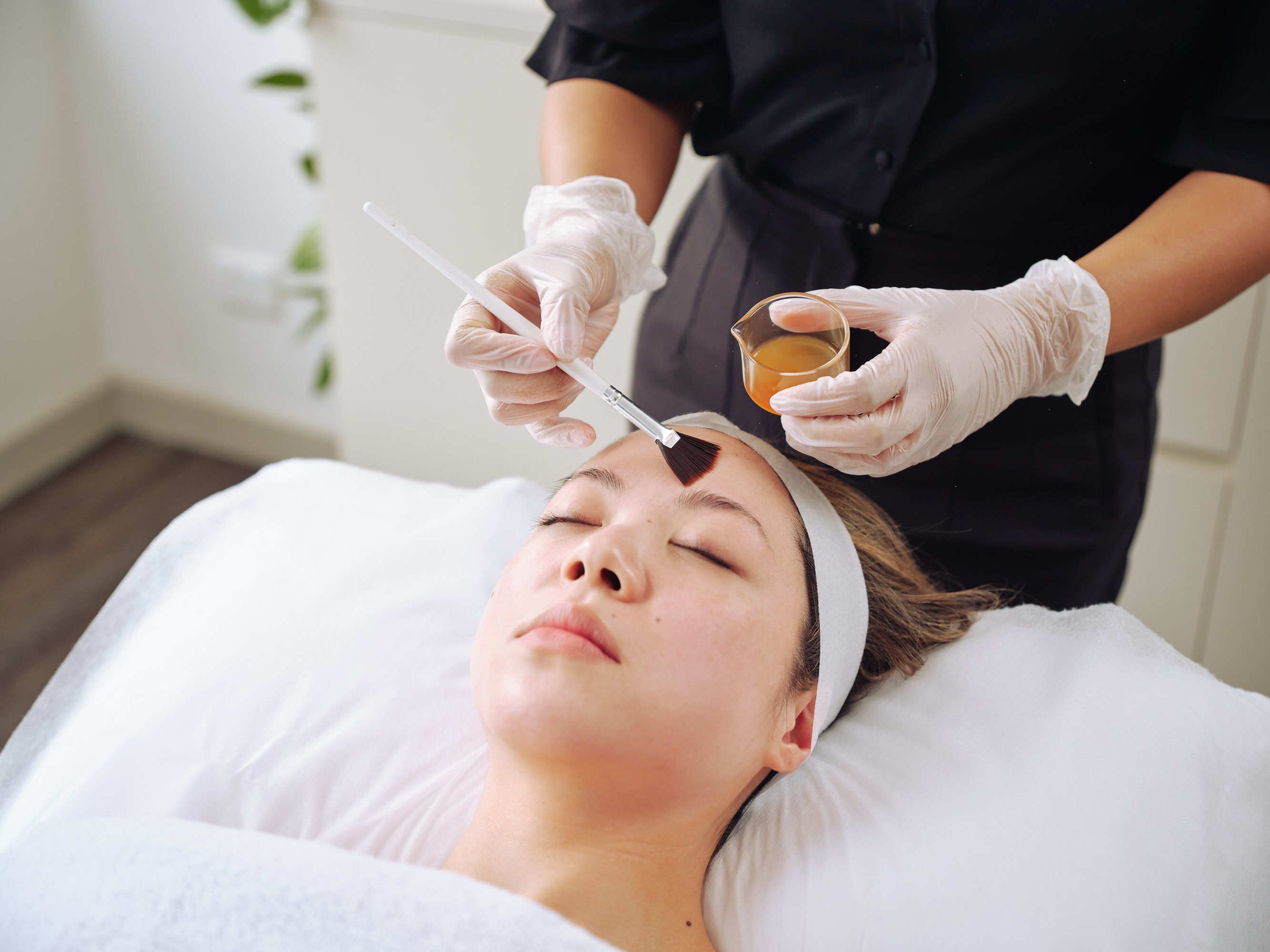
Even though the term implies a literal “peel,” your skin rarely flakes off dramatically. What is apparent, however, are the improvements beneath the exfoliated epidermis: smoother, more luminous skin.
Lactic acid is commonly used to treat hyperpigmentation, age-related spots, and other contributors to a dull, uneven complexion. Additional benefits shared by AHAs like lactic acid include more even skin tone and a diminished appearance of enlarged pores.
That said, compared with AHAs such as glycolic acid, lactic acid is somewhat gentler. This makes a lactic acid peel a preferable option for sensitive skin. It may also be suitable if you previously tried another AHA and found it too harsh.
Are side effects possible?
Although lactic acid is milder than some AHAs, it’s still a potent exfoliant.
Its resurfacing action increases your skin’s susceptibility to the sun’s ultraviolet (UV) rays, so diligent sunscreen use is essential. Be sure to apply sunscreen every morning and reapply throughout the day as needed.
Repeated unprotected sun exposure can lead to additional age spots, scarring, and may raise your risk of skin cancer.
Lactic acid peels can also provoke irritation, rashes, and itching. These reactions are generally mild and tend to subside as your skin acclimates. If symptoms persist beyond the first few uses, stop using the product and consult your doctor.
You should avoid lactic acid peels if you have:
- eczema
- psoriasis
- rosacea
If your skin is naturally darker, check with a dermatologist before trying a chemical peel. Chemical peels can increase the chance of post-inflammatory hyperpigmentation.
How to use a lactic acid peel
Directions vary by formulation and concentration. Always read the product instructions and adhere to the manufacturer’s guidance.
Purchase
For a mild at-home peel, seek a formula with around 5 percent lactic acid. Medium-strength peels typically range from 10 to 15 percent, while deeper (professional) peels utilize higher concentrations.
As a general guideline, higher concentration yields stronger effects. You may require fewer treatments with stronger peels, but any irritation that occurs can last longer.
Preparation and use
Performing a patch test before your first full-face application is important. This helps minimize the chance of adverse effects.
To perform a patch test:
- Apply a dime-sized amount of the product to the inside of your forearm.
- Cover the spot with a bandage and leave it undisturbed.
- If no irritation or redness occurs within 24 hours, the product is likely safe to use on the face.
- If you experience a reaction, stop using the product and consult a dermatologist if symptoms worsen or persist beyond a day or two.
Lactic acid peels are intended for evening use. Like other AHAs, lactic acid heightens sun sensitivity, so avoid morning application.
Protection
Daily sunscreen is essential while using lactic acid. For optimal protection, apply sunscreen each morning and reapply as necessary during the day. You may also use a moisturizer with SPF and a foundation that contains sun protection.
Lactic acid products to try at home
Lactic acid peels are commonly sold in drugstores, beauty retailers, and online shops.
Popular choices include:
- Dermalogica Gentle Cream Exfoliant. Formulated for more sensitive skin, this cream lactic acid exfoliant also includes salicylic acid. Together these ingredients help remove dead cells that contribute to dullness and pigmentation. You might also be interested in how it compares to other acids — see glycolic acid vs salicylic acid.
- Juice Beauty Green Apple Peel Full Strength. This comprehensive peel addresses wrinkles and dark spots with lactic acid and other AHAs. It also contains willow bark (a natural salicylic acid source) plus vitamins A and C. Not recommended for sensitive skin.
- Patchology Exfoliate FlashMasque Facial Sheets. These single-use lactic acid face sheets exfoliate dead skin to refine texture and appearance. They’re convenient to use with no rinsing required.
- Perfect Image Lactic Acid 50% Gel Peel. For deeper at-home resurfacing, this gel contains 50 percent lactic acid to improve complexion. The gel format helps prevent runoff. As a professional-grade peel, consult your dermatologist before use.
- QRx Labs Lactic Acid 50% Gel Peel. Another professional-strength option, this gel has a high 50 percent lactic acid concentration. Although marketed for professional outcomes, discuss it with your dermatologist to reduce the chance of adverse reactions.
Consider getting a professional lactic acid peel
While at-home lactic acid peels are available, the Mayo Clinic notes that deeper clinical peels produce the most dramatic and longer-lasting improvements. Their effects typically outlast OTC options, meaning fewer repeat treatments.
You may opt for a lactic acid peel from a dermatologist or skincare professional if OTC products aren’t delivering results but you’d prefer not to switch to a stronger AHA.
Before a professional lactic acid peel, discuss all medications you use and any skin sensitivity with your dermatologist. These factors help determine the appropriate peel strength and can prevent complications like irritation or scarring.
Also be aware that recovery from a professional lactic acid peel can take up to two weeks. Mild peels may cause side effects lasting around a day, but after a deeper peel your skin might need to be protected or bandaged for several weeks.
Lactic acid peels vary in price and are typically not covered by insurance since they’re cosmetic procedures rather than medically necessary treatments. You may, however, be able to arrange a payment plan with your provider’s billing office.
The bottom line
Lactic acid is used in mild chemical peels to even out skin tone. It can help with age spots, melasma, rough texture, and fine lines.
Although OTC options exist, consult a dermatologist before attempting a lactic acid peel at home, since certain skin conditions raise the risk of adverse effects.
If you do use an OTC peel, perform a skin patch test before full-face application and be diligent about sunscreen each morning and reapplying during the day.




















Leave a Reply
You must be logged in to post a comment.