Yes — sustaining a head injury can raise the likelihood of later developing schizophrenia or bipolar disorder. Damage to areas like the frontal lobes of the brain has been shown in some cases to trigger temporary psychotic symptoms.
The risk of a head injury contributing to schizophrenia or bipolar disorder tends to be higher in:
- individuals who experience a severe traumatic brain injury
- people with a family history of schizophrenia
- older adults
- women more so than men

Typical neurological signs after a head injury
Any substantial trauma to the brain can produce symptoms associated with schizophrenia, including hallucinations and delusional thinking.
Such injuries may also lead to diminished cognitive abilities, for example reduced attention span and problems with memory. Other psychiatric issues can emerge too, such as:
- depression
- anxiety
- sleep disturbances like insomnia
- bipolar disorder
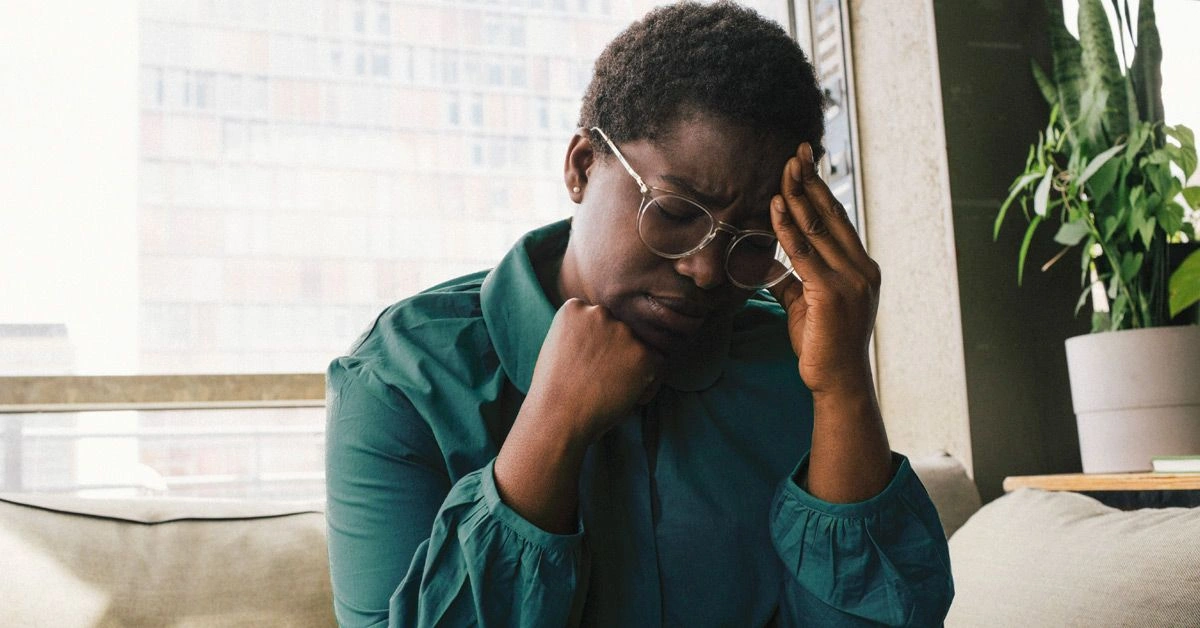
If you notice persistent changes in thinking or mood following a head injury, it’s important to seek evaluation since these symptoms can overlap with conditions often described as brain fried.
When to seek medical attention for a head injury
If you experience any of the following signs after a concussion or head trauma, contact medical services or have someone do so for you:
- repeated vomiting
- noticeable changes in behavior, such as unusual irritability
- a headache that won’t ease despite taking analgesics
- memory problems or confusion
Seek emergency care immediately (or have someone get it for you) if you lose consciousness and later regain it.
How to manage care after a head injury
If you sustain a head injury, phone a healthcare professional or have someone arrange medical care on your behalf. Clinicians can observe your progress and provide appropriate treatment.
Putting off medical assessment after head trauma can raise the risk of serious complications, including stroke or a coma.
There are several self-care measures you can use while recovering from a head injury, such as:
- applying an ice pack to the injured spot intermittently for short durations
- ensuring you get adequate rest
- using over-the-counter pain relievers like ibuprofen (Advil) if pain occurs
For additional related information, see our piece on headache after eating.





















Leave a Reply
You must be logged in to post a comment.