Nitric oxide plays key roles in your body, such as helping lower blood pressure, enhancing circulation, and improving exercise capacity. To elevate nitric oxide, include foods like beets, garlic, meats, leafy greens, and citrus in your diet.
Nitric oxide is an essential molecule produced within the body that influences many aspects of health.
It causes blood vessels to relax and widen to support adequate blood flow and may offer additional benefits, including better athletic performance, reduced blood pressure, and improved cognitive function.
Altering your diet is one of the simplest and most effective means to naturally raise levels of this important molecule.
Below are the top 10 foods that help boost nitric oxide.
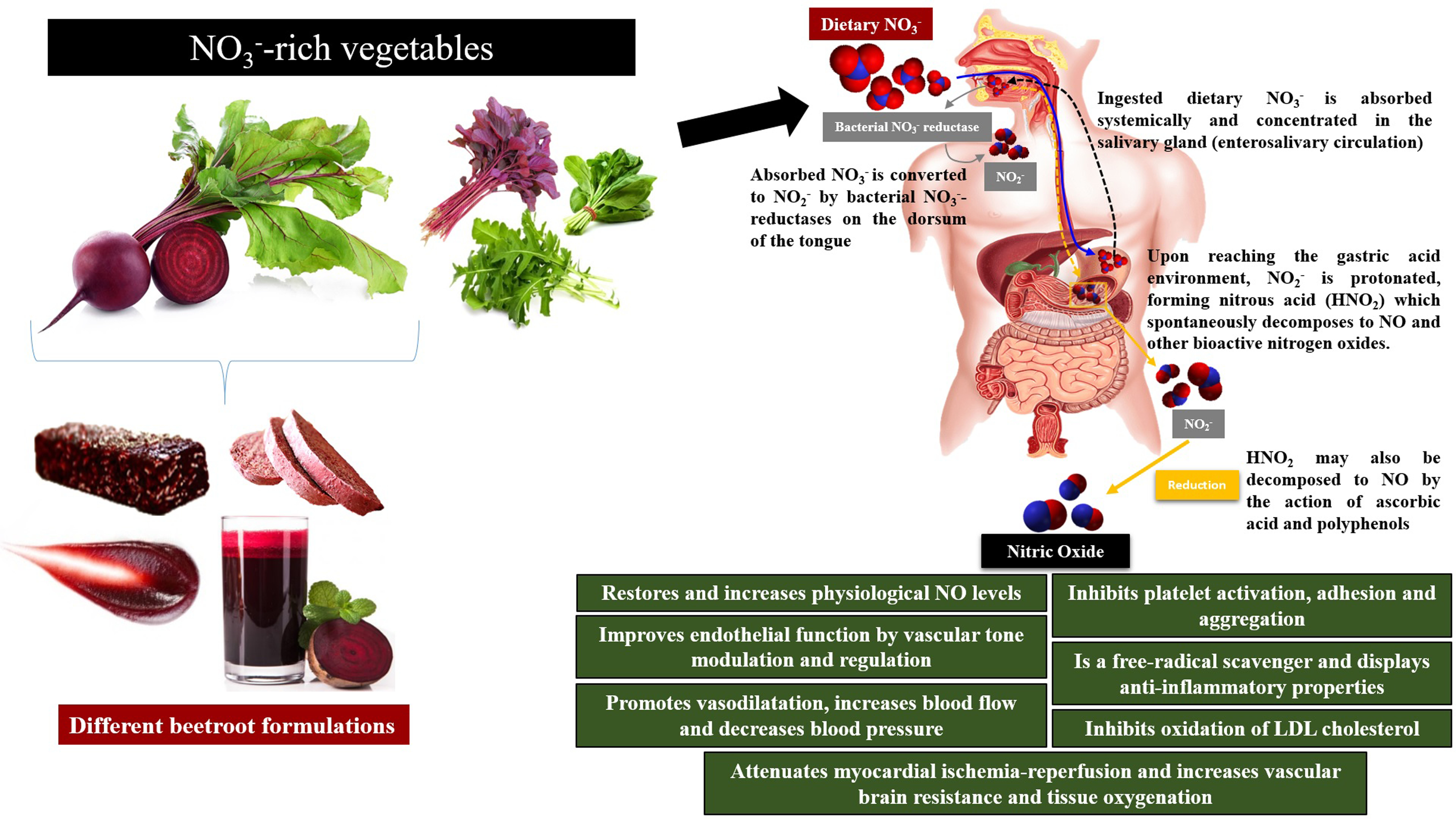
1. Beets
Beets are abundant in dietary nitrates, which the body can convert into nitric oxide.
In one study, consuming a beet juice supplement increased nitric oxide by 21% within 45 minutes.
Similarly, research showed that drinking 3.4 ounces (100 milliliters) of beet juice significantly elevated nitric oxide in both men and women.
Due to their high nitrate content, beets have been associated with several health advantages, such as improved cognitive performance, enhanced athletic output, and reduced blood pressure.
2. Garlic
Garlic can increase nitric oxide by stimulating nitric oxide synthase, the enzyme that converts the amino acid L-arginine into nitric oxide.
One study found that aged garlic extract helped reduce elevated blood lipids like cholesterol and triglycerides. Keep in mind that aged garlic extract or garlic oil differs from consuming fresh garlic.
A 2013 test-tube study also suggests aged garlic extract may enhance the amount of nitric oxide the body can use.
Both animal and human research indicate garlic’s capacity to raise nitric oxide may contribute to health improvements and can help support cardiovascular health and circulation.
3. Meat
Meat, poultry, and seafood are strong sources of coenzyme Q10 (CoQ10), a nutrient that appears to help preserve nitric oxide in the body.
Organ meats, oily fish, and muscle meats such as beef, chicken, and pork have the highest CoQ10 levels.
Research shows that adequate dietary CoQ10 not only protects nitric oxide but also may enhance athletic performance, reduce migraine frequency, and support heart health.
4. Dark chocolate
Dark chocolate is rich in flavanols, natural compounds with a wide array of health-promoting effects.
In particular, evidence shows that cocoa flavanols can help maintain healthy nitric oxide levels to support cardiovascular health and protect cells from oxidative stress.
One trial in 16 people found that consuming 30 grams of dark chocolate daily significantly increased blood nitric oxide concentrations.
Participants also experienced reductions in both systolic and diastolic blood pressure.
Owing to its high content of nitric oxide–supporting flavanols, dark chocolate is linked with improved circulation and lower blood pressure.
5. Leafy greens
Leafy greens such as spinach, arugula, kale, and cabbage are loaded with nitrates, which the body transforms into nitric oxide.
Regular intake of nitrate-rich vegetables helps sustain adequate nitric oxide levels in blood and tissues.
One 2020 study showed that a nitrate-rich meal containing leafy greens or beet juice similarly raised nitrate levels and significantly lowered both systolic and diastolic blood pressure.
Other evidence suggests that consuming high-nitrate leafy greens may be linked to a decreased risk of heart disease and cognitive decline.
6. Citrus fruits
Citrus fruits like oranges, lemons, limes, and grapefruit are excellent sources of vitamin C, a crucial water-soluble nutrient for overall health.
Vitamin C can raise nitric oxide by improving its bioavailability and supporting its absorption in the body.
Vitamin C may also increase levels of nitric oxide synthase, the enzyme required to make nitric oxide.
Studies indicate citrus consumption may be tied to improved cardiovascular markers and circulation. These effects may be partly due to these fruits’ capacity to enhance nitric oxide.
7. Pomegranate
Pomegranate contains potent antioxidants that shield cells from damage and help preserve nitric oxide.
One study found pomegranate juice effectively protected nitric oxide from oxidative deterioration while boosting its activity.
A trial in 60 people with type 2 diabetes suggested pomegranate juice offered some benefit in lowering blood pressure, though it did not demonstrate changes in lipid profiles.
Research has shown that antioxidant-rich pomegranate can improve blood flow, which may be particularly helpful for managing high blood pressure.
Additionally, one study reported pomegranate juice aided erectile dysfunction, but further human trials are needed to confirm these potential benefits of pomegranate juice and extracts.
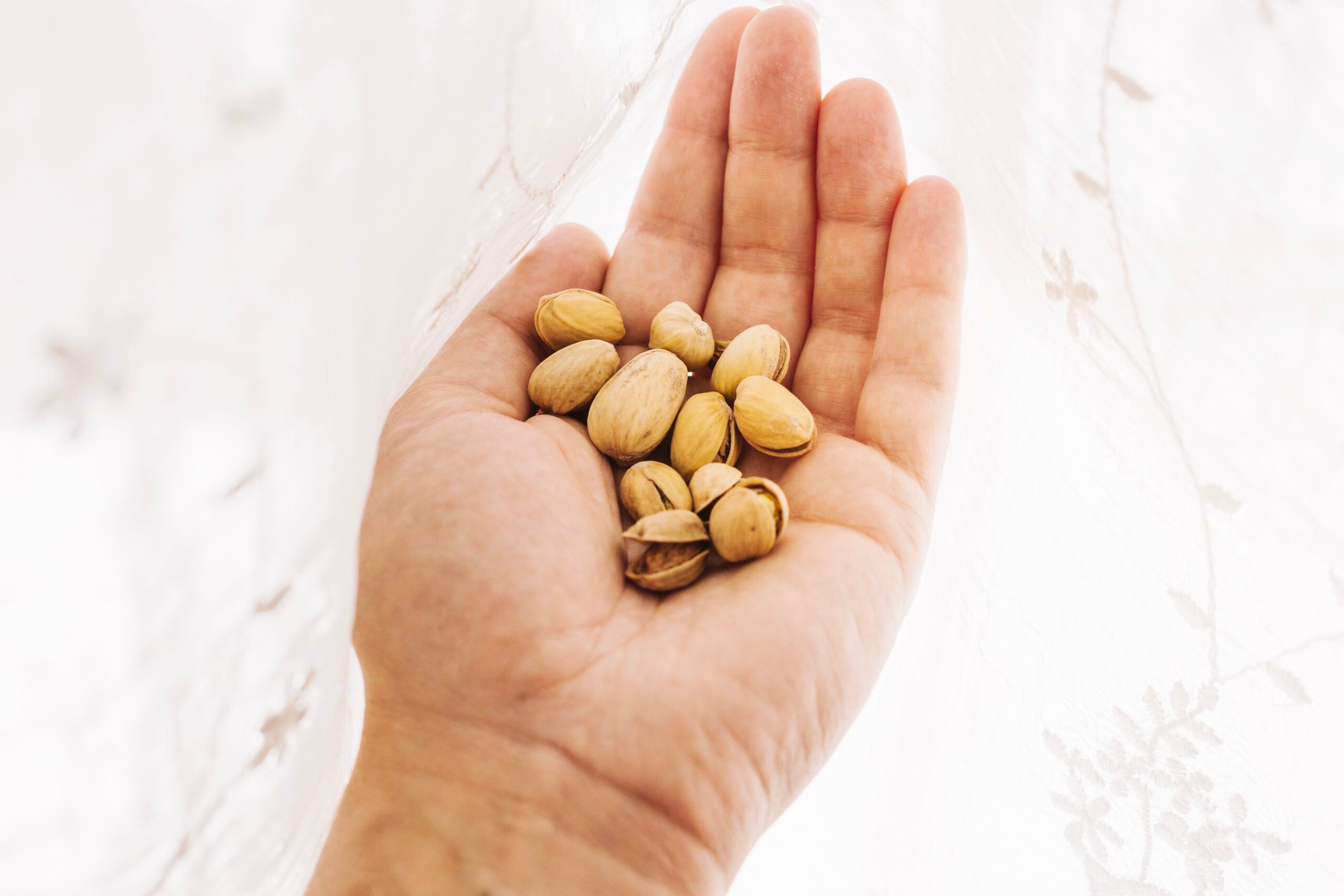
8. Nuts and seeds
Nuts and seeds are rich in arginine, an amino acid involved in nitric oxide synthesis.
Some studies suggest that consuming arginine from foods like nuts and seeds can raise nitric oxide levels in the body.
For example, research in 2,771 people showed that higher intake of arginine-rich foods correlated with elevated blood nitric oxide.
Because of their arginine content and strong nutrient profile, regular consumption of nuts and seeds has been associated with lower blood pressure, better cognitive function, and increased endurance.

9. Watermelon
Watermelon is among the best dietary sources of citrulline, an amino acid the body converts to arginine and subsequently to nitric oxide.
Research found that citrulline supplements stimulated nitric oxide production within hours, though health benefits may take longer to become evident.
A small 2016 study in 8 men showed that drinking 10 oz (300 mL) of watermelon juice for 2 weeks significantly improved nitric oxide bioavailability.
According to a review, increasing watermelon intake not only boosts nitric oxide but may also improve exercise performance, reduce blood pressure, and enhance circulation.
However, another study suggests citrulline supplements might be a more practical way to obtain these effects, since eating watermelon daily may not be feasible for everyone.
10. Red wine
Red wine contains numerous powerful antioxidants and has been associated with some health benefits.
Interestingly, some studies report that moderate red wine consumption can also increase nitric oxide levels.
A review of studies found that resveratrol in red wine is likely to benefit cardiovascular health by improving nitric oxide availability, though more clinical trials in humans are necessary.
For this reason, moderate red wine intake has been proposed to lower blood pressure and support heart health.
The bottom line
Nitric oxide is a vital compound involved in many facets of health, including blood pressure regulation, exercise performance, and brain function.
Making a few simple dietary substitutions is an easy and effective method to boost your nitric oxide levels naturally.
Eating a variety of fruits, vegetables, nuts, seeds, and quality protein sources can help you optimize nitric oxide while promoting overall well-being.






















Leave a Reply
You must be logged in to post a comment.