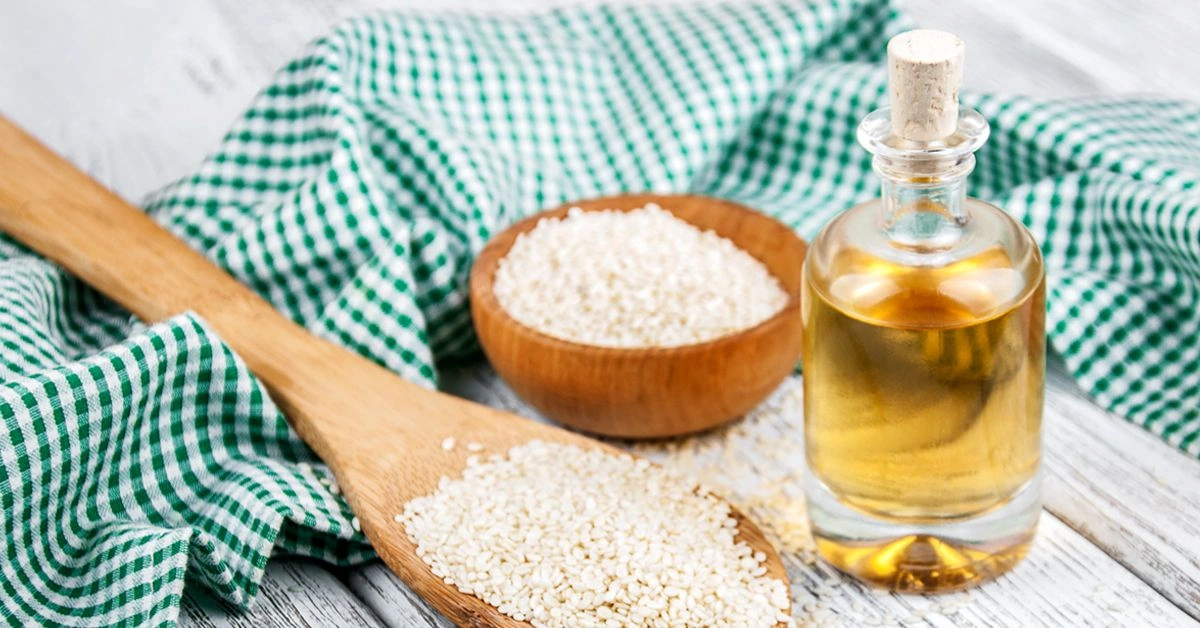
Sesame oil comes from the seeds of the flowering sesame plant, known scientifically as Sesamum indicum. Originally native to East Africa and India, these plants are now cultivated in many regions worldwide.

Thanks to its robust, nutty aroma and its rich content of mono- and polyunsaturated fats, sesame oil has become a favored cooking oil.
But is its usefulness limited to the kitchen? Can it be a suitable product for skincare? Continue reading to explore the characteristics of this oil and what it may — and may not — do for your skin.
What are the benefits of applying sesame oil to skin?
Sesame oil exhibits several traits that make it a potentially useful skincare ingredient:
- Antioxidant. It can neutralize damage from free radicals — unstable molecules that can impair skin cell structure.
- Antimicrobial. It may inhibit or destroy harmful microbes.
- Anti-inflammatory. It can help lower inflammation and swelling.
Sesame oil also scores moderately low on the comedogenic scale, an informal ranking of oils and butters by their pore-clogging potential. The scale runs from zero to five.
A score of zero means an oil is unlikely to clog pores, while five indicates a high likelihood of clogging them.
A 1989 study in the Journal of the Society of Cosmetic Chemists reported that refined sesame oil has a comedogenic rating of one, and unrefined sesame oil a rating of three. Oils that are non-comedogenic, like sesame oil, are often suitable for many skin types.
Because non-comedogenic oils are less likely to block pores, sesame oil might be suitable for acne-prone skin. Its anti-inflammatory actions could further aid in managing acne, although strong clinical evidence is limited.
Research on sesame oil for skincare is sparse, but some studies have found antioxidant, antimicrobial, and anti-inflammatory effects:
- A 2005 animal study showed that applying sesame oil topically may lower oxidative stress, which can damage cells and tissues.
- A recent animal study indicated that topical sesame oil aided healing of second-degree burn wounds.
- A small study found that sesame oil used with massage significantly reduced pain from limb injuries in emergency patients.
- There is some evidence that sesame oil can filter ultraviolet (UV) rays to a degree, but it should not replace sunscreens formulated for UV protection.
What nutrients does sesame oil contain?
Sesame oil is a source of vitamin E, which helps shield skin cells from environmental damage such as UV radiation, pollution, and toxins.
The oil also contains several phenolic compounds that contribute to its antioxidant and anti-inflammatory actions. These include:
- tocopherol
- pinoresinol
- sesamin
- sesamolin
- sesaminol
- sesamol
Additionally, sesame oil provides essential fatty acids that serve as effective moisturizers to keep skin soft, supple, and hydrated:
- oleic acid
- palmitic acid
- stearic acid
- linoleic acid
Is it safe to apply sesame oil to skin?
For most people, sesame oil is safe to use. As with any topical product — especially if you have sensitive skin — perform a patch test before widespread use.
To carry out a patch test:
- Clean and dry the upper inner arm near the elbow.
- Apply a small amount of sesame oil with a sterile cotton ball.
- Cover it with a gauze pad for 24 hours.
- If you experience tingling or itching, remove the gauze, wash the area, and stop using the oil.
- If there’s no irritation, keep the gauze on for the full 24 hours, then remove it.
- If the skin appears and feels normal, you’re likely not sensitive or allergic and can use the oil safely on your skin.
If you have a diagnosed sesame allergy, avoid using sesame oil.
How to use sesame oil
Sesame oil is a carrier oil, not an essential oil, so it does not require dilution before application.
Look for sesame oil that doesn’t contain additives or fillers. Check product labels to confirm purity and whether other ingredients are present.
You can use sesame oil generously for skin massage and moisturizing.
For acne or acne scarring, dab a small amount onto the affected areas with a cotton ball and leave it on overnight. Exfoliating first to remove dead skin cells may help the oil penetrate more effectively.
For guidance on complementary natural skincare options, you might be interested in exploring essential oils for skin and how carrier oils like safflower oil for skin compare.
Other uses for sesame oil
Beyond topical skincare, sesame oil has a variety of other uses:
- Cooking. Its gentle nutty flavor makes it ideal for stir-fries and dressings. Research suggests broader health advantages: one study reported that sesame oil might lower cholesterol and inflammation, another study found potential blood pressure–reducing effects, and a 2002 animal study suggested chemopreventive properties.
- Mouthwash. Its antibacterial traits make it useful for oil pulling, an Ayurvedic mouth-rinsing practice.
- Constipation relief. Anecdotally, diluted sesame oil may ease mild constipation. One method is mixing one to two tablespoons with water and drinking it twice daily.
- Hair and scalp care. The nutrients and properties that benefit skin can also nourish hair. Massage a small amount into the scalp and hair, focusing on dry ends. Leave it on at least an hour, then rinse.
The bottom line
Sesame oil, with its antioxidant, anti-inflammatory, and antibacterial properties, can support skin health in multiple ways and may be particularly helpful for acne-prone skin and scarring.
Its anti-inflammatory effects also contribute to potential systemic benefits such as lowering blood pressure and cholesterol.
If you’re considering using sesame oil on your skin, consult your physician or dermatologist to determine whether it’s appropriate for your skin type and needs.





















Leave a Reply
You must be logged in to post a comment.