Boosting your protein consumption and adding resistance training to your schedule can assist in reducing body fat while increasing muscle tissue.

Body composition describes the proportion of fat versus fat-free components (muscle, bone, and water) present in your body.
Assessing body composition provides a clearer picture of health than screening tools that only use weight and height, such as body mass index (BMI).
That’s because the percentage of body fat relative to muscle mass more accurately indicates your overall health status than weight or BMI alone.
Consequently, body recomposition emphasizes altering body composition instead of just focusing on weight.
Rather than a temporary diet, body recomposition is a way of life where nutrition and exercise strategies produce favorable shifts in your fat-to-muscle ratio.
Recomposition literally means “to form again or in a different way,” which is why the phrase “body recomposition” is used.
When implemented properly, body recomposition adjusts your body’s makeup so you carry less fat and more muscle.
How does body recomposition work?
Body recomposition is a lifestyle approach rather than a short-term diet. It aims to preserve and build muscle while simultaneously reducing fat. Achieving this requires changes to both eating habits and workout routines.
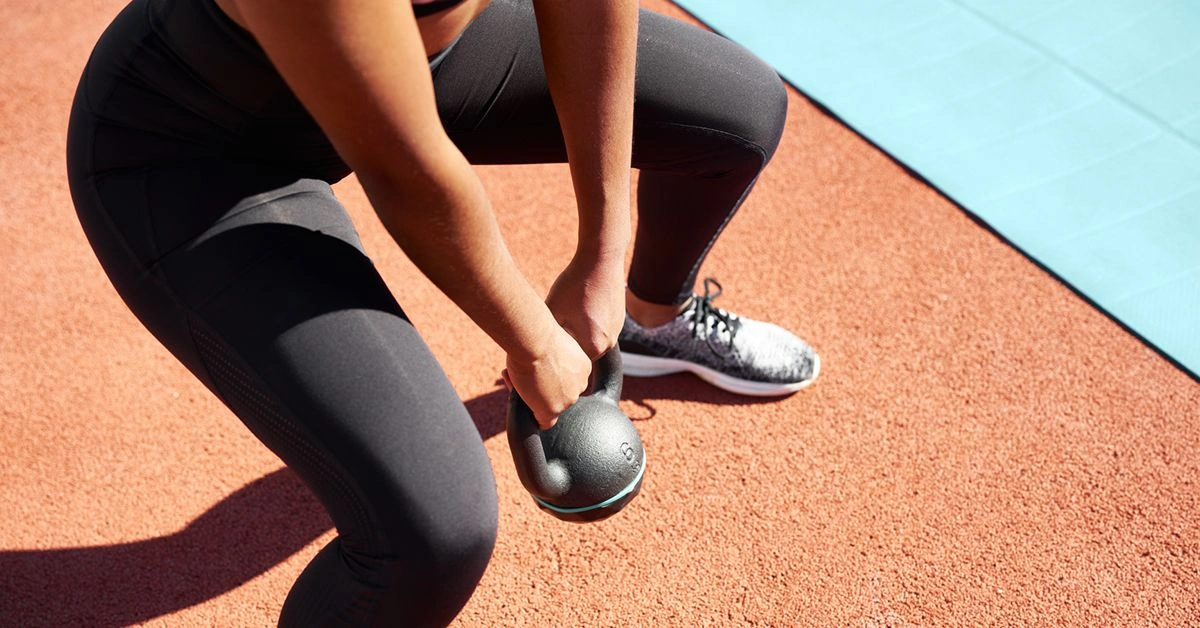
While aerobic activity matters for weight management and general health, strength training is essential for changing body composition.
Additionally, a protein-rich dietcan support fat loss while aiding muscle development.
Approaches to body recomposition may differ based on your specific objectives.
For instance, a lean bodybuilder aiming to add muscle while cutting fat will require different nutritional and training strategies than someone with overweight or obesity seeking to lose fat and enhance muscle definition.
The positive news is that body recomposition strategies can benefit anyone, regardless of how much fat they want to shed or muscle they wish to build.
How to lose fat
Fat loss requires a calorie deficit, which you can create by eating fewer calories, increasing energy expenditure, or combining both.
However, drastically slashing calories through very low-calorie diets or performing endless cardio sessions doesn’t necessarily protect muscle mass.
To lose fat while maintaining or even increasing your musculature, it’s more effective to moderately reduce calories and include muscle-building exercises, particularly resistance training.
The quality of your diet also influences fat loss. Eating a protein-focused diet has been shown to decrease fat while preserving lean tissue. Consider adding more protein-rich choices such as:
- chicken breast
- turkey breast
- cottage cheese
- lean beef
- lentils
- eggs
How to gain muscle
Although losing fat is important, retaining or increasing muscle is crucial for shifting your body composition.
Concentrating solely on diet while ignoring exercise can lead to muscle loss.
It’s essential to pair a nutritious, muscle-supporting diet with a training program that encourages muscle growth and retention.
The importance of protein
When your aim is to build muscle, nutrition plays a pivotal role.
A balanced eating plan centered on whole foods—plenty of produce, healthy fats, complex carbs, and protein—is ideal for everyone, no matter their fitness aims.
Those working on changing their body composition often need to raise their protein intake, since research indicates a high-protein diet is important for supporting muscle gain.
It’s advisable to spread protein sources across meals by consuming protein-dense foods like eggs, poultry, and dairy throughout the day.
Best exercises for gaining muscle
Alongside a protein-forward, whole-foods diet, adding resistance training to your program is vital.
Strength training uses resistance to increase strength and muscle mass; lifting weights is a common example.
If your objective is to build muscle and lose fat, specialists advise a training routine that includes at least two days of resistance work per week.
It’s suggested to gradually raise the weight by no more than 10% weekly so the body can adapt, helping to lower the likelihood of injury or overtraining.
Examples of effective movements include:
- squats
- lunges
- push-ups
- stair-climbing
The bottom line
Body recomposition centers on building muscle while shedding fat.
Consider increasing protein intake and engaging in strength training at least twice weekly.
Techniques for body recomposition are useful for everyone, from high-level athletes to people simply aiming for a healthier physique.




















Leave a Reply
You must be logged in to post a comment.