Even though it’s a tiny organ, the gallbladder can develop problems. While conditions affecting the gallbladder range in seriousness, some may contribute to sensations of abdominal bloating.
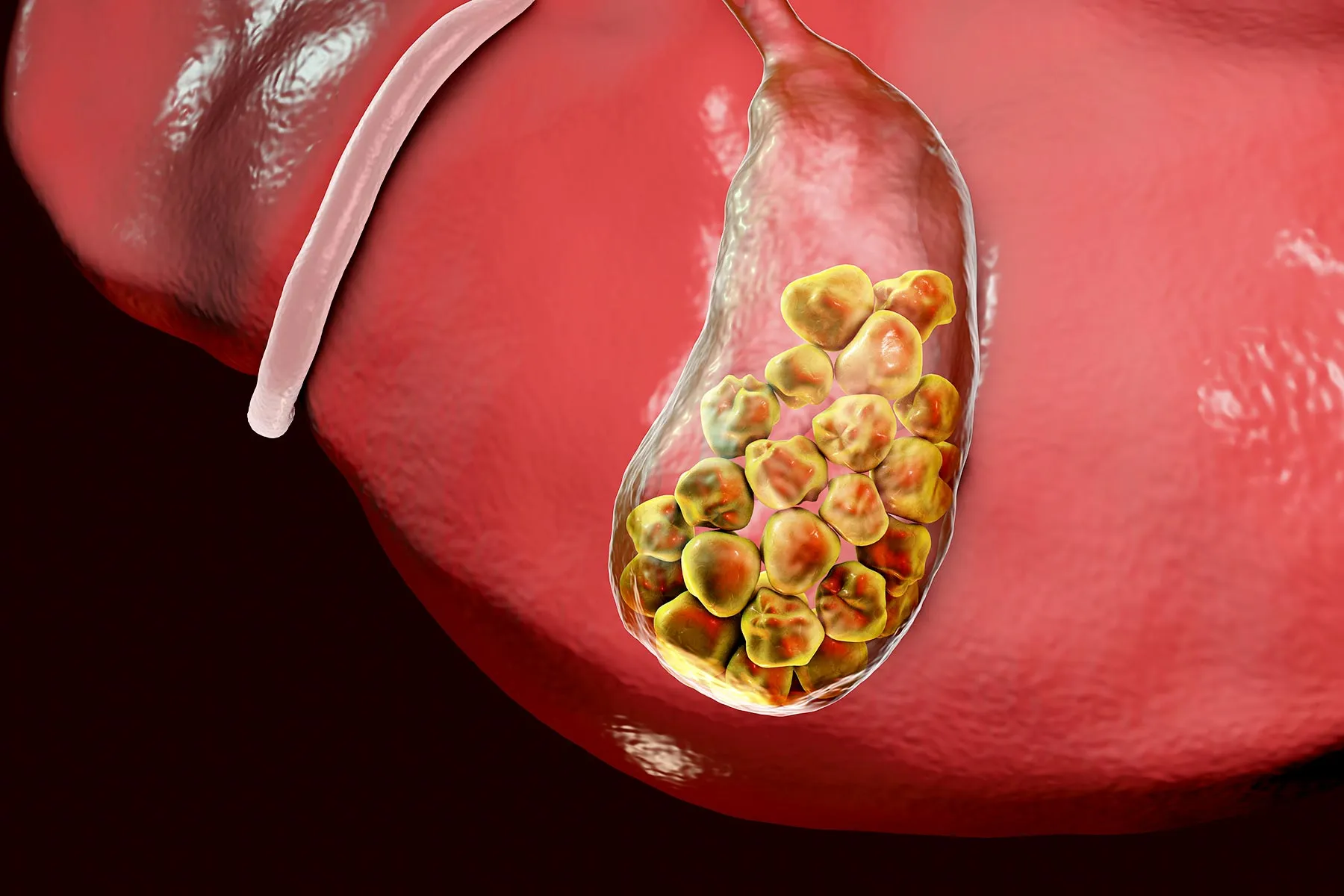
The gallbladder is a small component of your digestive tract that stores bile. Measuring only about 3–4 inches long, it plays a key role in helping your body break down fats from food.
Not every instance of bloating is serious, and only a minority are caused by gallbladder disorders. Read on to learn which gallbladder conditions can lead to bloating and other important details about each.
Which gallbladder problems might cause bloating?
Inflammation or other conditions that produce swelling or blockages in the gallbladder can trigger bloating. Below is an overview of gallbladder issues that may cause abdominal distension and the other symptoms they commonly produce.
Gallstones and gallbladder attacks
Gallstones are hardened deposits made of cholesterol or bilirubin that form in the gallbladder. They can harden and become lodged in the bile ducts in your upper-right abdomen.
Gallstones typically remain symptom-free until they obstruct a bile duct. Although 10–20% of people may have gallstones, it’s estimated that only about 1–3% develop symptoms.
If a gallstone blocks the ducts, it can cause biliary colic, often referred to as a gallbladder attack. Intense pain is a frequent sign of an attack. Bloating (abdominal distension) is less typical but can occur.
Other possible signs of a gallbladder attack include:
- pain that may radiate to your back or shoulder
- tenderness in the abdomen
- nausea
- vomiting
A gallstone might slip back into the gallbladder or pass through the duct. If it remains stuck, additional symptoms can include:
- fever
- chills
- pale stools and dark urine
- yellowing of the skin and eyes (jaundice)
Cholecystitis
Cholecystitis describes inflammation of the gallbladder. The most frequent cause is a gallstone blocking the cystic duct. Like gallbladder attacks, pain is the dominant symptom and it may travel up to the right shoulder.

An outward swelling or bloated feeling in the abdomen can accompany acute cholecystitis. People with chronic cholecystitis have also reported bloating and increased gas.
Other symptoms of this condition can include:
- abdominal tenderness
- pain that worsens with deep breaths
- fever
- nausea
- vomiting
- sweating
- loss of appetite
Biliary dyskinesia
Biliary dyskinesia is a disorder in which the gallbladder fails to empty properly. This can lead to dysmotility, where the muscles of the digestive tract don’t function normally, affecting digestive processes. Dysmotility can produce abdominal pain and cramping. Nausea, vomiting, and bloating are additional possible symptoms.
Gallbladder cancer
Gallbladder cancer is uncommon; most cases are adenocarcinomas. Abdominal swelling is one potential symptom, though other signs are more typical.
The most frequently observed symptoms of gallbladder cancer include:
- palpable masses on the right side of the abdomen
- abdominal pain
- jaundice
- nausea
- vomiting
Other signs of a poorly functioning gallbladder
Besides bloating, gallbladder problems can cause a variety of other symptoms, such as:
- pain
- fever
- nausea or vomiting
- jaundice
- changes in appetite
- unintended weight loss
- changes in urine or stool
When to see a doctor
Seek urgent medical attention if you have severe abdominal pain lasting more than a few hours or if you develop a high fever or jaundice.
Make an appointment if you experience unexplained bloating with abdominal pain or any other possible gallbladder symptoms. These signs might indicate a gallbladder issue, but they could also reflect other serious conditions, such as:
- appendicitis
- gastroesophageal reflux disease (GERD)
- hepatitis
- pancreatitis
- peptic ulcers
How are gallbladder-related causes of bloating treated?
Treatment varies based on the cause, and removal of the gallbladder is a common option.
Gallstone treatments
If gallstones don’t cause symptoms, they often don’t need treatment.
For stones stuck in the bile duct, procedures such as lithotripsy or endoscopic retrograde cholangiopancreatography (ERCP) may be used. These procedures are sometimes combined with antibiotics to address fever or chills.
Symptomatic gallstones are often treated surgically by removing the gallbladder via laparoscopic or open cholecystectomy.
For patients who cannot tolerate surgery, such as some elderly individuals, doctors may try medications to dissolve gallstones.
Cholecystitis treatment
Acute cholecystitis typically requires hospital care, sometimes for up to a week. During hospitalization you may receive intravenous fluids and be asked to fast.
Antibiotics are given if there’s a gallbladder infection. Many people with cholecystitis are advised to have their gallbladder removed.
Biliary dyskinesia treatment
The most common treatment for biliary dyskinesia is cholecystectomy — surgical removal of the gallbladder.
Gallbladder cancer treatment
Treatment depends on the cancer’s type and stage and may include one or more of the following:
- surgical removal of the gallbladder
- radiation therapy
- immunotherapy
- chemotherapy
- targeted drug therapies
Common questions about the gallbladder and warning signs
If you’re worried about bloating or gallbladder disease, consider discussing these frequently asked questions with your healthcare provider.
What does it feel like when your gallbladder is irritated?
Severe pain in the upper-right abdomen that can radiate to the back or shoulder is a common indication of gallbladder trouble. Depending on the cause, pain may be intermittent or persist for several hours, often worsening at night. You may also experience general malaise and nausea.
Can the gallbladder be inflamed without stones?
Although gallstones often precipitate inflammation, biliary dyskinesia can also cause an inflamed gallbladder. Acalculous cholecystitis—gallbladder inflammation without stones—may result from infection, decreased bile flow, or impaired blood supply.
What are symptoms of a swollen gallbladder?
A swollen gallbladder can produce abdominal pain or a feeling of fullness. Depending on the cause, other signs may include nausea, vomiting, chills, and fever.
Can gallstones make you feel tired or lightheaded?
Fatigue can accompany gallstone symptoms and other gallbladder disorders. Some people also report dizziness, though strong clinical evidence is limited.
That said, dizziness can be a potential side effect of certain medications used to treat gallstones, such as oral bile acid agents.
Do gallstones cause weight gain?
Gallstones range widely in size — from tiny, sand-like particles to stones as large as a golf ball. While bloating can occur with gallstones, true weight gain is unlikely. Obesity, however, is a risk factor for developing gallstones.
Which antibiotics treat a gallbladder infection?
Physicians may choose from several antibiotics to treat a gallbladder infection, including:
- ceftriaxone (Ceftrisol Plus)
- levofloxacin (Levaquin)
- metronidazole (Flagyl, Nuvessa)
- piperacillin/tazobactam (Zosyn)
Can gallstones cause gas and bloating?
Gallstones can sometimes be associated with bloating. However, gas and abdominal distension are more commonly seen in gallbladder disorders broadly, which may be precipitated by gallstones.
Takeaway
Bloating is usually due to excess gas or overeating, but it can occasionally stem from underlying medical conditions such as gallbladder disease. If bloating is accompanied by intense abdominal pain, fever, or other concerning symptoms, seek medical attention.






















Leave a Reply
You must be logged in to post a comment.