If you notice redness, flushing, or a runny nose after eating a bowl of oatmeal, you might be allergic or sensitive to a protein present in oats called avenin.

Both oat allergy and oat sensitivity provoke an immune response. The body creates antibodies to fight what it perceives as a foreign invader — in this case, avenin.
Some people who develop symptoms after consuming oats may not be reacting to oats themselves but instead could have gluten sensitivity or celiac disease.
Gluten is a protein found in wheat. Oats naturally do not contain gluten; however, they are frequently cultivated and processed in facilities that also handle wheat, rye, and other gluten-containing grains.
Cross-contact among these products can lead to trace gluten in oat items. If you need to avoid gluten, ensure any oat product you consume or use is labeled gluten free. For more on this, see is oat milk gluten free.
Gastric upset after eating oats may also occur if you’re unusually sensitive to high-fiber foods. Keeping a food diary can help you determine whether you have an avenin allergy or a different issue.
Symptoms
Oat allergy is relatively uncommon but can affect infants, children, and adults. Reactions can range from mild to severe and may include:
- red, irritated, itchy skin
- rash or irritation inside the mouth
- scratchy or sore throat
- runny nose or nasal stuffiness
- itchy, watery eyes
- nausea
- vomiting
- diarrhea
- abdominal pain
- difficulty breathing
- anaphylaxis
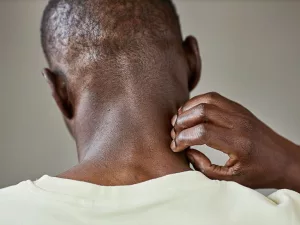
Oat sensitivity tends to produce milder symptoms that may develop more slowly. With repeated exposure, these symptoms can become chronic and may include:
- digestive irritation and inflammation
- diarrhea
- fatigue
In infants and young children, oat reactions can trigger food protein–induced enterocolitis syndrome (FPIES), which affects the gastrointestinal tract and can cause vomiting, dehydration, diarrhea, and poor growth.
If FPIES is severe or persistent, it can lead to lethargy and malnutrition. A variety of foods — not only oats — can provoke FPIES.
Topical use of oat-containing products can also cause skin issues. A 2007 study in children with atopic dermatitis found a notable proportion had allergic skin reactions to products containing oats, such as lotions.
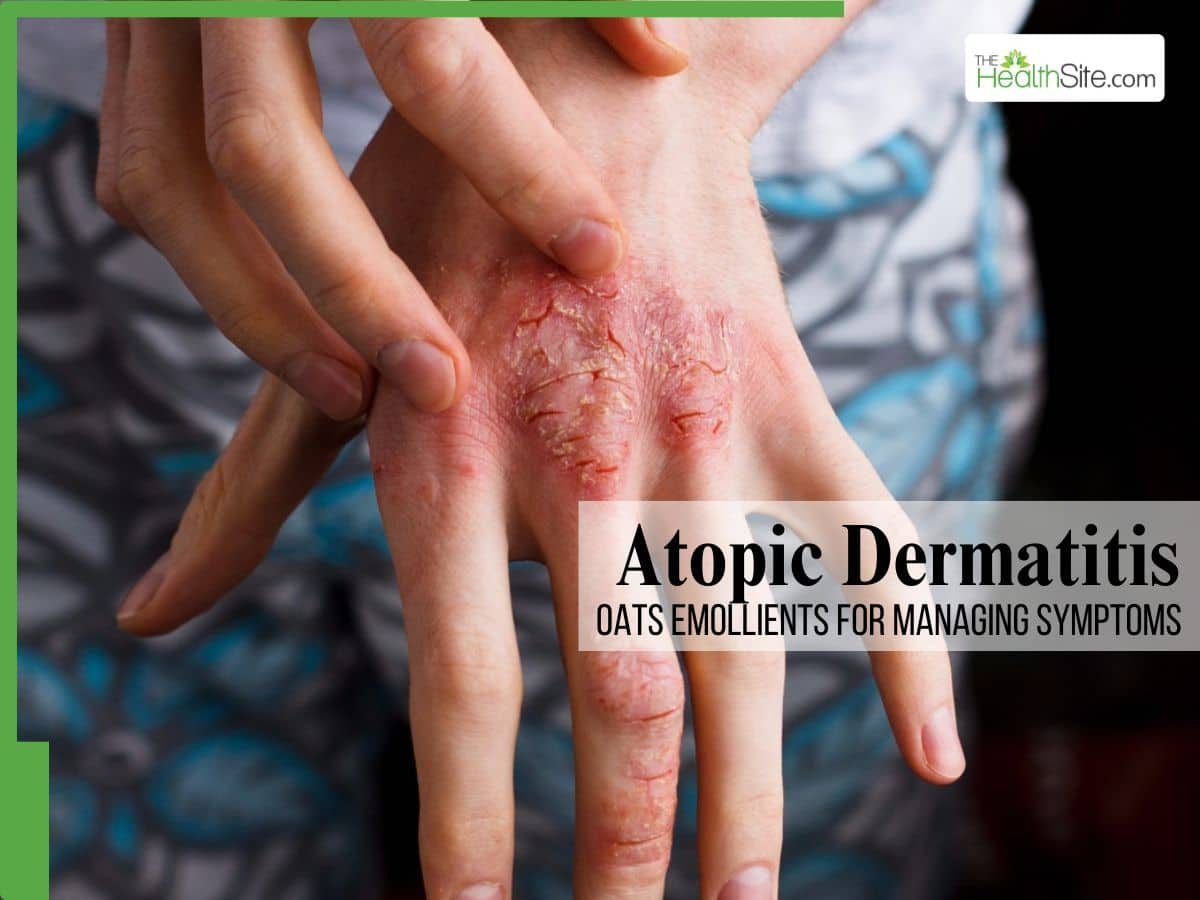
Adults may likewise develop skin reactions if they are allergic or sensitive to oats and apply products containing oat ingredients.
Treatment
If you’re allergic or sensitive to avenin, avoiding oats in foods and personal care products is essential. Read labels for terms like oats, oat powder, and avenin. Items to avoid include:
- oatmeal baths
- oatmeal-based lotions
- muesli
- granola and granola bars
- porridge
- oatmeal
- oat cookies
- beer
- oatcakes
- oat milk
- horse feed containing oats, like oat hay
Often, mild allergic reactions to oats can be eased with an oral antihistamine. For skin reactions, topical corticosteroids might provide relief.
People concerned about oat-related weight changes might look into oat weight gain for more context on oats and body weight.
Diagnosis
Several tests can identify food allergies, including to oats. Common diagnostics include:
- Skin prick test (scratch test). This assesses reactions to multiple allergens simultaneously. A clinician places tiny amounts of allergens, plus histamine and saline or glycerin, on the forearm and uses a lancet to introduce them under the skin to observe responses. The procedure is brief and typically takes 20 to 40 minutes.
- Patch test. Allergens are applied on adhesive patches placed on the back or arm for up to 48 hours to detect delayed allergic responses to oats.
- Oral food challenge. Under medical supervision, you ingest progressively larger amounts of oats to determine if a reaction occurs. This should only be performed in a facility equipped to manage severe allergic reactions.
When to see your doctor
If you experience a severe allergic reaction to oats, such as breathing difficulty or anaphylaxis, seek emergency medical help immediately.
As with any food allergy, these reactions can escalate quickly but may be halted with an epinephrine auto-injector (commonly called an EpiPen).
Even if you administer epinephrine and symptoms abate, call 911 or go to the nearest emergency room right away after an anaphylactic episode.
Common signs of anaphylaxis include:
- a sudden drop in blood pressure
- hives or intensely itchy skin
- wheezing or shortness of breath
- swelling of the tongue or throat
- nausea
- vomiting
- diarrhea
- weak, rapid pulse
- dizziness
- fainting
Takeaway
Oat sensitivity or allergy is uncommon. Those affected have an immune response to avenin, a protein present in oats.
People with gluten sensitivity or celiac disease may react to oats because of cross-contamination during growing or processing.
An oat allergy can produce potentially serious conditions in infants and children and may worsen atopic dermatitis.
If you suspect you or your child is allergic or sensitive to oats, avoid oat-containing products and consult your healthcare provider.
If you live with food allergies, consider using resources such as allergy-management apps for guidance on dining out, recipes, and more.




















Leave a Reply
You must be logged in to post a comment.