Overview
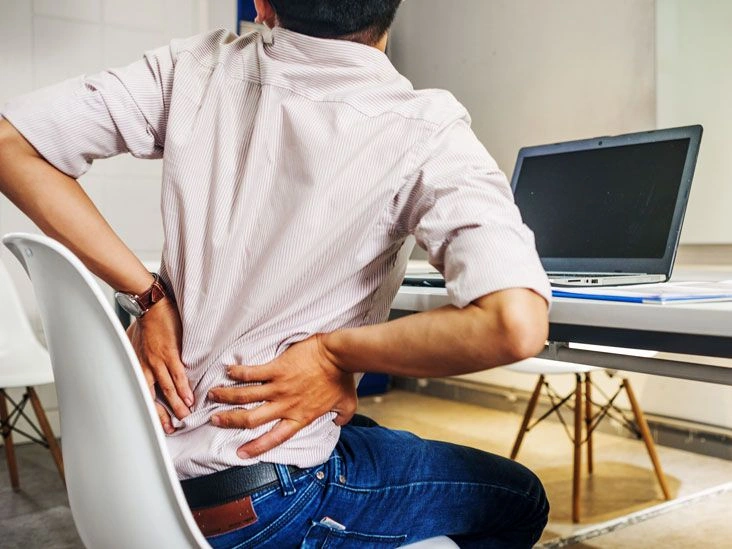
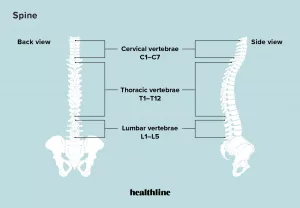
Back discomfort — especially in the lower back — is a frequent complaint. The sensation can vary from a dull ache to sharp, stabbing pains. Back pain may arise from a sudden injury or from a long-standing condition that causes persistent distress.
Dizziness can accompany pain. Dizziness describes a feeling that the surroundings are rotating. Like back pain, dizziness is commonly reported.
Dizziness may present in several ways beyond a spinning sensation. You might feel light-headed, as if you’re floating or about to faint. You could also have trouble maintaining your balance. Each of these sensations can stem from multiple causes.
There are many potential reasons for back pain. Your back is responsible for lifting, twisting, stabilizing, and absorbing shocks for your body. Those roles make it vulnerable to a variety of injuries. The fragile vertebrae along your spine encase the nerves of your spinal cord. A displaced bone or supportive disk can press on nerves and trigger pain.
In uncommon cases, back pain with dizziness may indicate a serious condition, such as a stroke or a brain bleed. Symptoms like double vision, slurred speech, numbness, and severe balance problems can signal a medical emergency.
If you develop back pain and dizziness during a blood transfusion, these may be signs of a severe transfusion reaction. Notify your healthcare team right away.
Below are 11 possible reasons for experiencing both back pain and dizziness.

Pregnancy
A typical full-term pregnancy lasts about 40 weeks. Numerous factors can influence a pregnancy’s course. Women who obtain early diagnosis and prenatal care are more likely to have a healthy pregnancy and deliver a healthy infant. Read more about pregnancy.
Endometriosis
Endometriosis is a condition in which tissue similar to the lining of the uterus grows outside the uterine cavity. The lining of the uterus is called the endometrium. Read more about endometriosis.
Osteoarthritis
Osteoarthritis (OA) is the most prevalent form of arthritis. It’s also called degenerative joint disease, degenerative arthritis, or wear-and-tear arthritis. Read more about osteoarthritis.
Fibromyalgia
Fibromyalgia is a chronic disorder featuring widespread muscle and bone pain, areas of tenderness, and general fatigue. Read more about fibromyalgia symptoms.
Sciatica
Sciatica describes pain that can range from moderate to severe in the back, buttocks, and legs. You may also notice weakness or numbness in these regions. Read more about sciatica.
Whiplash
Whiplash happens when the head is rapidly forced backward and then forward with significant force. This injury commonly follows rear-end car crashes. Read more about whiplash causes.
Ectopic pregnancy
With an ectopic pregnancy, the fertilized egg does not implant in the uterus. Instead, it may attach to a fallopian tube, the abdominal cavity, or the cervix. Read more about ectopic pregnancy.
Subarachnoid hemorrhage
Subarachnoid hemorrhage (SAH) describes bleeding into the subarachnoid space — the area between the brain and the coverings of the brain. Read more about subarachnoid hemorrhage.
Stroke
A stroke occurs when brain tissue is deprived of oxygen because a brain blood vessel ruptures and bleeds, or because a blockage interrupts blood flow. Brain cells begin to die within minutes, causing a stroke. Read more about stroke symptoms.
Abdominal aortic aneurysm
The aorta is the body’s largest artery. If the aortic wall weakens, it can bulge outward like a small balloon. When this happens in the portion of the aorta located in the abdomen, it’s called an abdominal aortic aneurysm (AAA). Read more about abdominal aortic aneurysm.
ABO incompatibility reaction
An ABO incompatibility reaction can happen if you are transfused with the wrong blood type. It’s an uncommon but serious and potentially life-threatening immune response to incompatible blood. Read more about ABO incompatibility reaction.
When should I seek medical help?
Call 911 or get someone to drive you to the emergency department if you suspect a stroke or heart attack. Other warning signs include confusion, chest pain, and weakness on one side of the body. Severe back pain and dizziness accompanied by loss of sensation in the legs is also an emergency.
Contact your doctor right away if:
- your back pain and dizziness don’t improve with home remedies after three days
- you experience hearing loss or worsening symptoms
- you develop back pain and dizziness while receiving a blood transfusion
Seek urgent medical advice if back pain and dizziness begin after starting a new medication.
How are back pain and dizziness treated?
Treatment depends on the underlying cause. Rest after an injury can often reduce back pain. Physical therapy exercises that stretch and strengthen your back may help lessen dizziness tied to severe pain.
Sometimes symptoms require more advanced interventions, such as injections for pain relief or surgery to relieve nerve compression. Your physician may prescribe medicines to control dizziness. Antihistamines like diphenhydramine (Benadryl) and meclizine (Antivert) can also help treat dizziness.
How can I care for back pain and dizziness at home?
If your symptoms are injury-related, resting and applying ice to your back can reduce pain and swelling. Always wrap ice in a cloth. Limit applications to no more than 10 minutes at a time to avoid damaging your skin.
You can also use over-the-counter pain relievers such as ibuprofen (Advil) or naproxen (Naprosyn) to ease back pain.
How can I prevent back pain and dizziness?
Using safe lifting techniques when moving heavy items can help prevent acute back injuries. Regular exercise keeps your back flexible and strong, lowering your risk of injury.
Keeping a healthy weight also helps reduce back pain. Excess weight places additional strain on the body and can cause pain. Being overweight raises the risk of cardiovascular events like stroke or heart attack.
Smoking negatively affects the spine and can lead to earlier back problems. Quitting smoking can improve your overall health in many ways.



















Leave a Reply
You must be logged in to post a comment.