Perfectionism and anxiety often intersect, with perfectionistic individuals more prone to experiencing anxiety and anxiety disorders. Cultivating mindfulness and employing other techniques can be crucial for managing unrealistic expectations.
For some people, anxiety and perfectionism are connected.
Perfectionism is a personality disposition defined by excessively high standards and expectations. While a degree of perfectionism can drive achievement, it is frequently fueled by a fear of making mistakes. When perfectionism becomes extreme, it can be damaging.
Anxiety is an emotional state marked by worry-filled thoughts, tension, and physical responses like a faster heart rate or elevated blood pressure. It typically emerges in anticipation of a perceived future threat. When anxiety begins to disrupt daily functioning, it may indicate a diagnosable anxiety disorder.
Perfectionism and anxiety can be linked because perfectionists often worry about living up to their stringent standards. Yet the connection is nuanced.

Is being a perfectionist a symptom of anxiety?
Perfectionism can be a manifestation of anxiety, but the link is somewhat reciprocal. Perfectionistic tendencies can provoke anxiety, and anxiety can reinforce perfectionism. Constantly striving to fulfill excessive standards often heightens anxious feelings.
Anxiety presents differently across individuals, but common signs include:
- trouble focusing
- rapid or racing thoughts
- disturbed sleep
- changes in appetite
- feeling restless
- fast breathing or heart palpitations
- persistent preoccupations (obsessive-compulsive disorder)
- sudden sensations of panic or impending doom
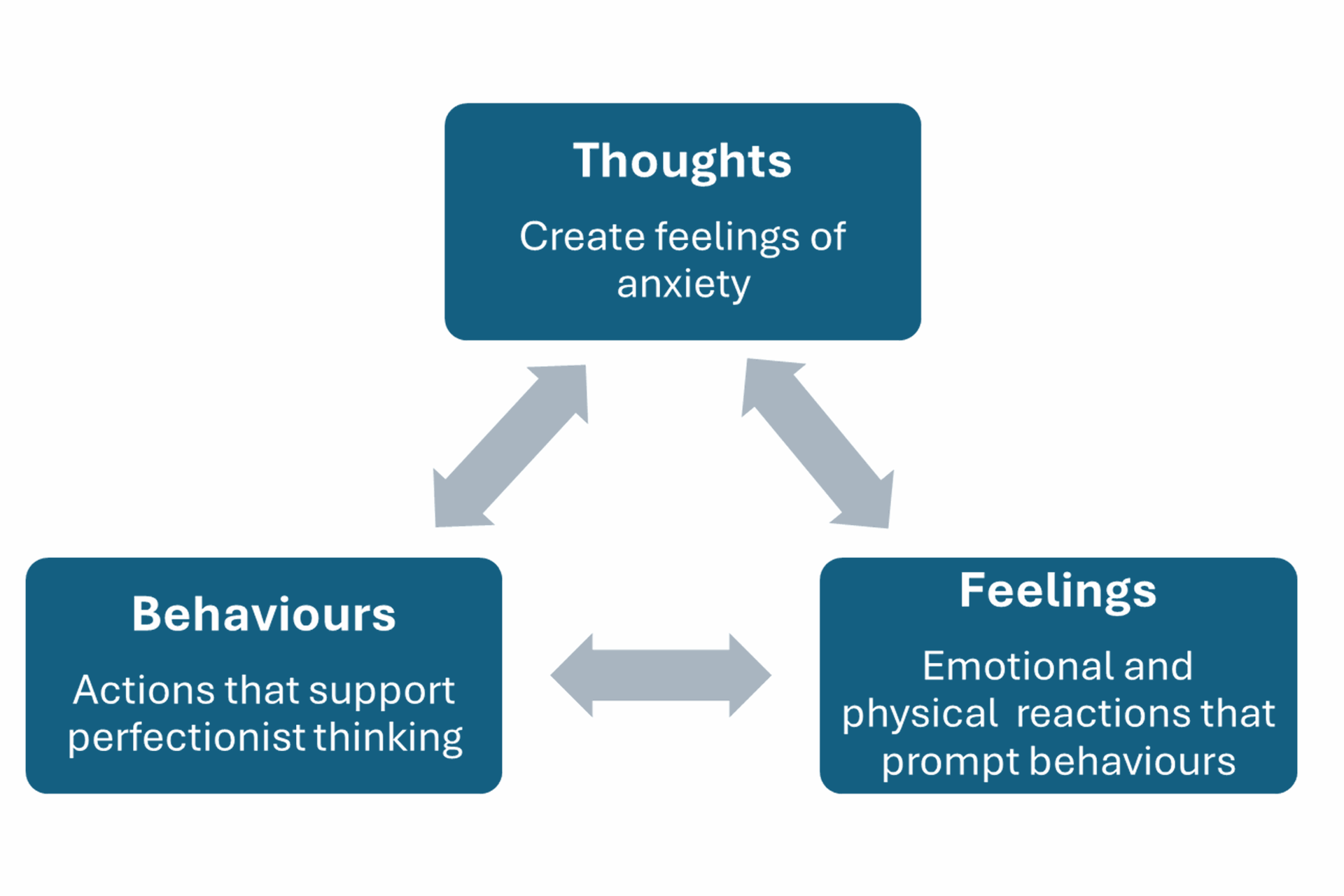
What is the perfectionism-anxiety cycle?
The perfectionism-anxiety loop can feel like a repetitive pattern of diminishing self-worth and continually raising the bar for yourself.
- You may begin by setting goals that are unrealistic.
- Because the objectives are unattainable, you often fail to reach them.
- The pressure to be flawless can lead to procrastination and decreased productivity.
- Self-criticism lowers your self-esteem, which can trigger anxiety and depressive symptoms.
- You may then try to compensate by tightening your standards and renewing the process.
Perfectionists may apply these expectations to relationships as well, sometimes unconsciously demanding the same standards from others. This ongoing perfectionism-anxiety cycle can harm interpersonal connections and keep goals out of reach.
How do you treat anxiety and perfectionism together?
There are several approaches to address anxiety and perfectionistic thinking and to help interrupt the perfectionism-anxiety loop.
If perfectionism and anxiety are impairing your everyday life, seeking assistance from a qualified professional is advisable. Each person’s situation is unique, so try different strategies to find what works best for you.
- Embrace imperfection: Engage in activities that aren’t outcome-focused, like playing a sport or creating art without aiming for excellence. Although it may feel uncomfortable, you may discover that mistakes don’t cause catastrophe.
- Practice mindfulness: Observing how you respond to your expectations can keep you grounded in the present and lessen perfectionism’s impact on social anxiety.
- Learn to compromise: Adopting more attainable standards for yourself can help move you away from all-or-nothing thinking.
- Exposure therapy: Gradually confronting uncertainty and fears with the support of a trained therapist can help you set realistic aims and tolerate imperfection.
- Cognitive behavioral therapy: CBT can help you spot unhelpful thought patterns and build healthier coping mechanisms, as well as modify reactions to triggering situations.
- Seek professional support: A therapist can pinpoint your particular concerns and recommend objective strategies for improvement. If you don’t have a clinician, ask your primary care provider for referrals.
Perfectionism and other disorders
Perfectionism is associated with more than just anxiety. A 2022 study indicated that perfectionistic traits correlate with various mental health issues, including:
- social anxiety
- eating disorders
- depression
- anxiety disorders
- obsessive-compulsive personality disorder
- suicidal thoughts
Takeaway
Perfectionism and anxiety often feed into one another. The drive to be flawless can generate anxiety, and anxious feelings can foster perfectionistic behavior.
Mindfulness can be an effective skill for recognizing triggers and deciding when to alter habitual patterns. Working with a mental health professional can provide direction for improving your situation.























Leave a Reply
You must be logged in to post a comment.