Failing a stress test happens when you’re unable to complete it because of exhaustion or other limiting factors. Abnormal findings can point to an underlying issue, such as coronary artery disease or an arterial blockage.
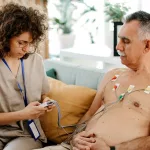
A stress test — often called an exercise stress test or treadmill test — is a diagnostic exam that assesses how the heart performs under stress, usually while you’re exercising.
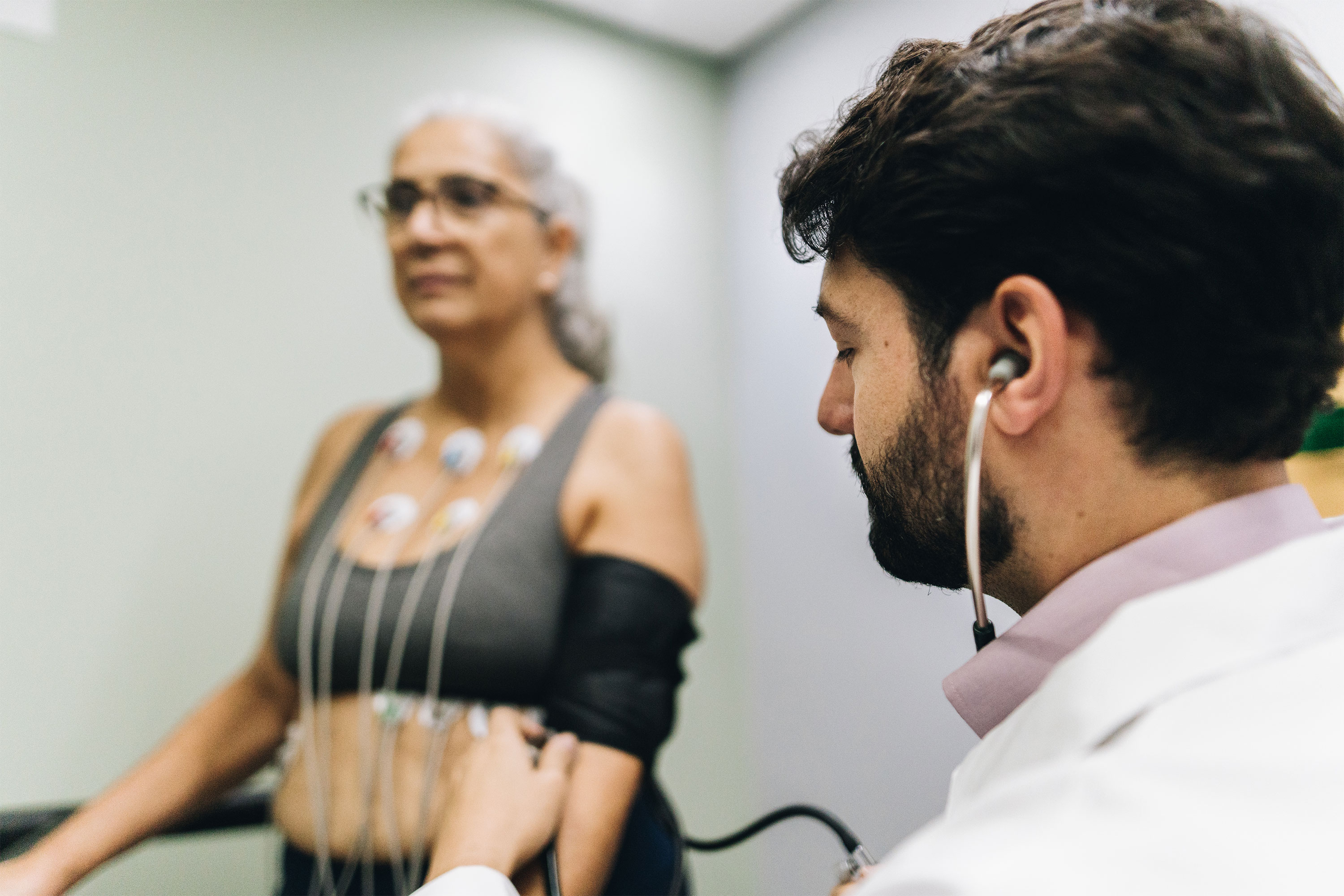
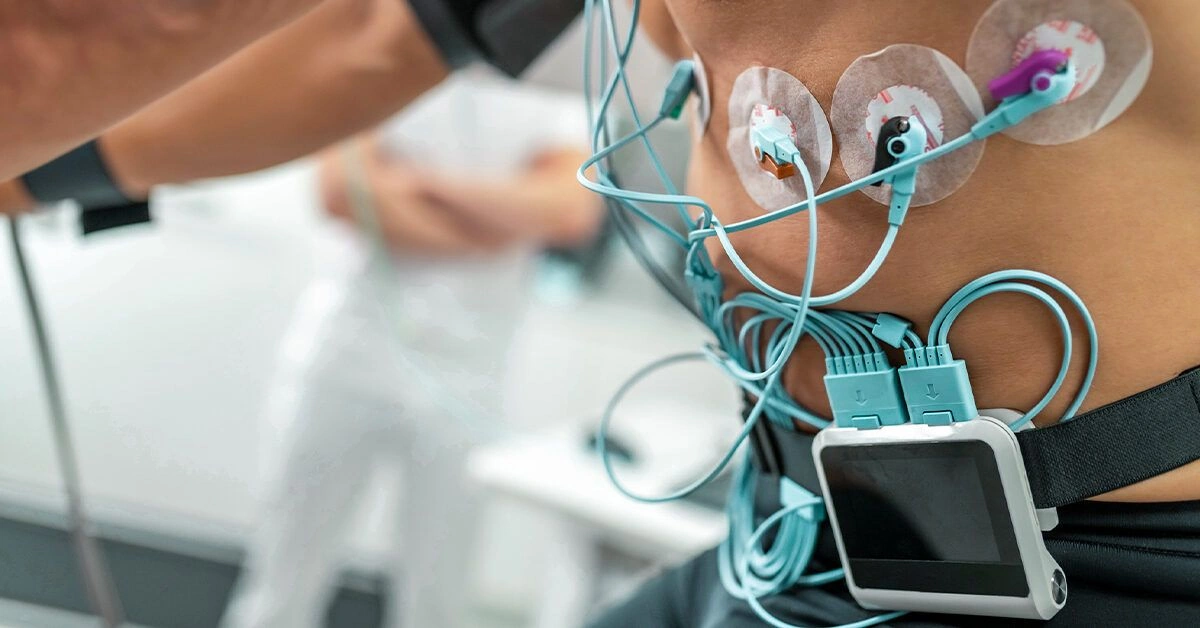
During the exam, a clinician will ask you to walk or jog on a treadmill or pedal a stationary bike. Meanwhile, they track your heart rate, blood pressure, and other vital signs using an electrocardiogram (EKG) device.
“Failing” and an “abnormal” outcome are two possible categories of stress test results. A negative result, by contrast, means no concerning abnormalities were observed.
Read on to understand more about abnormal stress test findings and what they could mean for your cardiovascular health.
What does it mean to “fail” a stress test?
Failing a stress test signifies that you cannot achieve or maintain the target heart rate during the exercise portion. This may stem from physical constraints like joint pain, breathing problems, or from cardiac issues such as coronary artery disease.
If you cannot complete the exercise, the clinician may suggest a pharmacologic stress test. In that evaluation, a medication such as adenosine is given intravenously to mimic the heart’s response to exercise, allowing physicians to assess cardiac function without physical exertion.
What does it mean if a stress test is “abnormal”?
During a stress test, the clinician observes various vital signs to evaluate how your heart responds to physical activity, including:
- heart rate
- blood pressure
- cardiac rhythm
- any symptoms you experience during the test, such as chest discomfort, breathlessness, or lightheadedness
An abnormal stress test result can indicate an underlying cardiac problem, like coronary artery disease, that might need additional evaluation or treatment. However, “abnormal” does not always imply a severe cardiac condition.
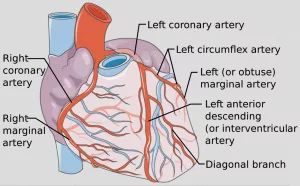
These findings can also point to a narrowing or blockage in the arteries that supply blood to the heart, which raises the risk of myocardial infarction.
What is considered a “normal” or negative result?
A stress test is considered normal (negative) when your heart rate, blood pressure, and rhythm remain within expected ranges and there are no signs of impaired blood flow to the heart or other markers of cardiac disease.
What happens after an abnormal stress test?
The follow-up after an abnormal stress test depends on the precise abnormalities found and your medical background. Your clinician might order further testing, such as a coronary angiogram, if there’s concern about blocked arteries to determine the location and severity of any blockages.
In a coronary angiogram, a contrast dye is injected into the coronary vessels and X-ray images are taken to create a detailed map of the coronary arteries.
If the abnormal stress test stems from other causes, such as an arrhythmia, additional evaluations may be needed to investigate the root cause, including:
- Echocardiogram: A noninvasive ultrasound test that produces images of the heart. An echocardiogram helps clinicians assess heart structure and function and detect abnormalities.
- Cardiac CT or MRI: Advanced imaging studies that offer high-detail views of the heart and vessels, helping to evaluate blood flow and identify blockages or other structural issues.
Depending on these supplementary test results, your provider may suggest medications, lifestyle modifications, or invasive procedures to treat any conditions affecting cardiac performance.
When might you need a stress test?
A physician may recommend a stress test if you have risk factors for or symptoms suggestive of heart disease.
Symptoms and signs that could prompt testing include:
- chest pain or pressure
- shortness of breath
- palpitations or irregular heartbeat
A family history of heart disease or other cardiovascular risk factors can also lead a clinician to order an exercise stress test. Doctors might also request one before you begin strenuous physical activity or while you’re undergoing treatment for heart conditions.
Frequently asked questions about abnormal stress test results
Can a stress test detect a blockage?
Yes. Stress tests are generally effective at detecting blockages that obstruct about 70% or more of the coronary arteries that supply blood to the heart muscle. A blockage is a narrowing or obstruction of these arteries, often caused by plaque buildup (atherosclerosis).
What happens if a blockage is suspected after a stress test?
If a stress test suggests possible coronary artery blockages, your doctor will likely order additional studies, such as a coronary angiogram, to confirm and clarify the diagnosis.
Can a stress test be abnormal even without a blockage?
Yes. An abnormal stress test result can occur without an actual coronary blockage. Various factors can produce abnormal findings, including certain medications (for example, beta-blockers) that alter heart response during exercise.
The bottom line
Stress testing is a common tool to evaluate cardiac function and identify potential heart disease. An abnormal stress test may signal conditions such as coronary artery disease that warrant further investigation.
Although an abnormal result can be worrisome, it does not automatically indicate a major heart problem. Based on your situation, your clinician may recommend further diagnostic tests — such as a coronary angiogram — to find the underlying cause and guide appropriate treatment.
For related procedures and recovery information, you may also find helpful guidance on what happens during a tooth cleaning and options for wisdom teeth pain relief, which discuss procedural expectations and pain management strategies in other medical contexts.




















Leave a Reply
You must be logged in to post a comment.