Diamine oxidase is an enzyme that aids in degrading surplus histamine in the body. While additional studies are necessary to confirm its effectiveness and optimal dosing, current research has not reported harmful side effects.
Diamine oxidase (DAO) is an enzymatic compound and dietary supplement often used to address symptoms linked to histamine intolerance.
Taking DAO supplements may provide certain advantages, but the body of evidence remains limited.
This article examines DAO supplementation, covering potential benefits, dosing considerations, and safety concerns.
What Is DAO?
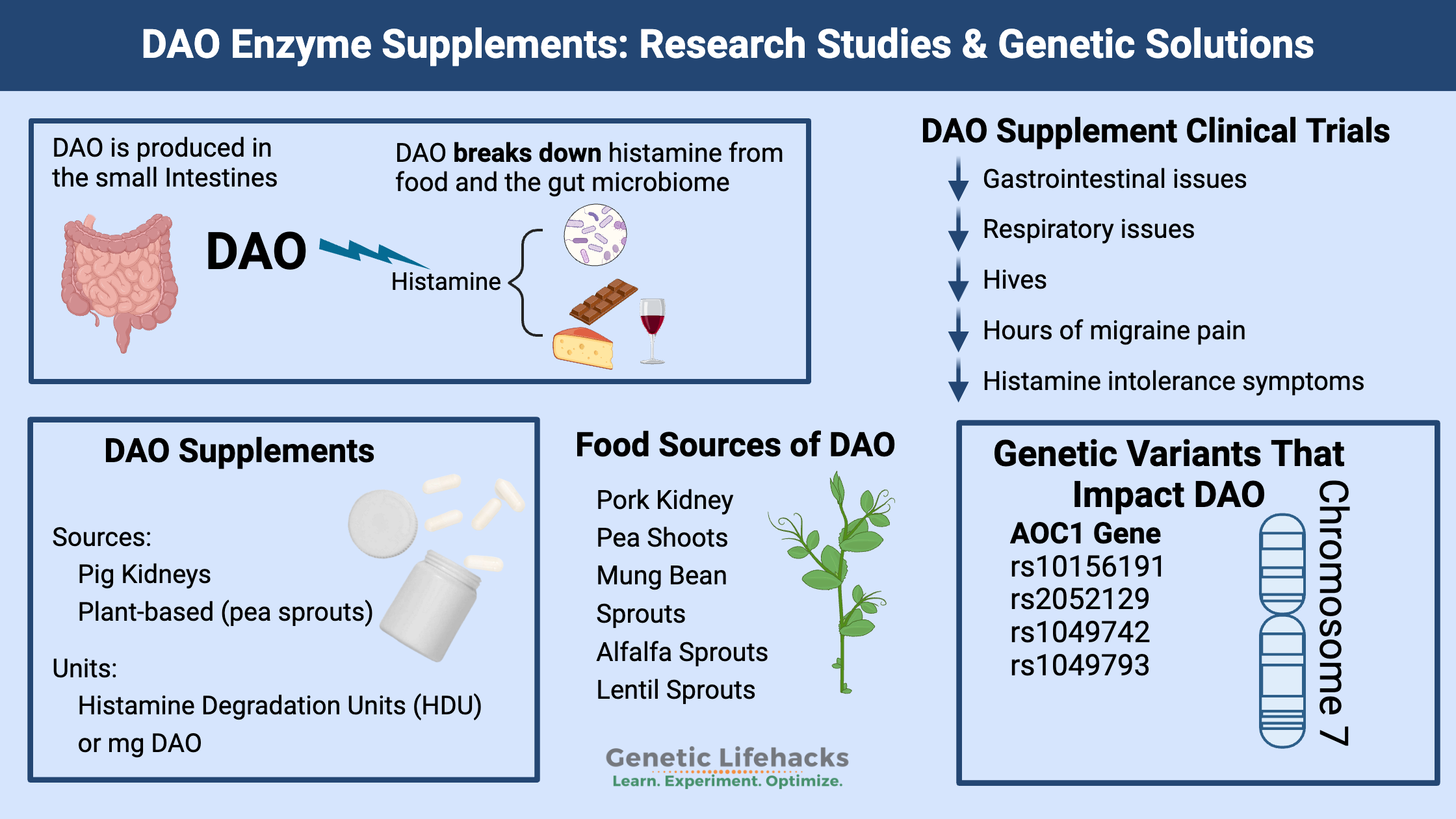
Diamine oxidase (DAO) is a digestive enzyme produced in organs including the kidneys, thymus, and the small intestinal lining.
Its chief role is to metabolize excess histamine present in your system (1).
Histamine is a naturally occurring molecule that helps regulate certain functions of the digestive, nervous, and immune systems.
If you’ve ever had an allergic response, you’re likely familiar with common signs tied to elevated histamine, such as nasal congestion, itchy skin, headaches, and sneezing.
Histamine is also present in foods. It appears naturally in items that are aged, cured, or fermented — for example cheese, wine, pickles, and smoked meats (1).
DAO helps maintain histamine at healthy levels to prevent unpleasant histamine-related symptoms.
SummaryDiamine oxidase (DAO) is an enzyme that breaks down extra histamine in the body, helping reduce symptoms such as nasal congestion, itchy skin, headaches, and sneezing.
DAO Deficiency and Histamine Intolerance
Histamine intolerance is a clinical condition that arises when histamine levels in the body become elevated.
One proposed cause of histamine intolerance is insufficient DAO activity.
When DAO activity is low, the body cannot effectively metabolize and remove excess histamine. Consequently, histamine accumulates and produces various physical symptoms.
Symptoms of histamine intolerance often mimic allergic reactions. They vary from mild to severe and can include:
- nasal congestion
- headaches
- itchy skin, rashes, and hives
- sneezing
- asthma and breathing difficulties
- irregular heartbeat (arrhythmia)
- diarrhea, abdominal pain, and other digestive complaints
- nausea and vomiting
- low blood pressure (hypotension)
Multiple factors may reduce DAO activity or increase histamine production, such as genetic variants, alcohol consumption, certain medications, small intestinal bacterial overgrowth, and consuming large quantities of histamine-rich foods.
Diagnosing histamine intolerance can be challenging because its symptoms are non-specific and overlap with other conditions (1).
If you suspect histamine intolerance, consult a qualified healthcare professional to properly evaluate the causes of your symptoms before attempting self-diagnosis or treatment.
SummaryHistamine intolerance can result from low DAO activity and lead to numerous unpleasant symptoms that often resemble an allergic response.
Potential Benefits of DAO Supplements
DAO deficiency and histamine intolerance can be managed in various ways, including DAO supplementation.
Preliminary studies indicate DAO supplements might reduce certain symptoms of histamine intolerance, such as headaches, dermatologic reactions, and gastrointestinal issues.
Digestive Symptoms
In a 2-week trial of 14 individuals with histamine intolerance who experienced abdominal pain, bloating, or diarrhea, 93% reported improvement in at least one digestive symptom after taking 4.2 mg of DAO twice daily.
Migraine Attacks and Headaches
A 1-month trial with 100 participants diagnosed with DAO deficiency found that those taking daily DAO experienced a 23% shorter duration of migraine attacks compared with placebo.
Skin Rash
In a 30-day study of 20 people with chronic spontaneous urticaria and DAO deficiency, participants receiving the supplement twice daily reported meaningful symptom relief and a lower need for antihistamine drugs.
While these studies imply that DAO supplementation may reduce or resolve deficiency-related symptoms, results are not guaranteed for everyone.
Ultimately, larger and more rigorous studies are needed to reach firm conclusions.
SummaryEarly research suggests DAO supplements may help relieve some symptoms associated with DAO deficiency and histamine intolerance — including migraines, skin rashes, and digestive complaints — but further study is required.
Not a Cure
Scientific knowledge of histamine intolerance and DAO insufficiency remains in its early stages.
Many variables influence the production of DAO and histamine across different tissues. Fixing the underlying issues is not as simple as taking a DAO supplement (1).
DAO supplements act to degrade histamine that comes into the body from external sources, such as foods and drinks.
They do not affect histamine produced internally, which is metabolized by a different enzyme called N-methyltransferase.
Although DAO supplements may relieve symptoms by lowering external histamine exposure, evidence that they cure histamine intolerance or DAO deficiency is lacking.
If you have been diagnosed with histamine intolerance or suspect it, work with a qualified healthcare provider to create a tailored treatment plan based on your individual needs and health objectives.
SummaryTo date, no scientific evidence demonstrates that DAO supplements cure DAO deficiency or histamine intolerance.
Nutritional Therapies for DAO Deficiency
Histamine intolerance and DAO insufficiency are multifactorial conditions influenced by numerous contributors that affect symptom severity.
At present, dietary modification is one of the primary strategies used to manage these conditions.
Since some foods contain varying amounts of histamine, changing your diet can reduce exposure to histamine-rich foods and to items that may inhibit DAO activity.
Enhancing DAO Function
Nutritional approaches aimed at improving histamine tolerance and DAO activity focus on ensuring adequate consumption of nutrients involved in histamine breakdown, such as copper and vitamins B6 and C.
Some evidence also suggests that sufficient intake of healthy fats and micronutrients — including phosphorus, zinc, magnesium, iron, and vitamin B12 — may support DAO activity.
Following a diet largely composed of low-histamine foods may decrease histamine exposure and its accumulation. Low-histamine options include:
- fresh meat and fish
- eggs
- most fresh vegetables — excluding spinach, tomatoes, avocado, and eggplant
- most fresh fruits — excluding citrus and certain berries
- oils such as coconut and olive oil
- grains like rice, quinoa, corn, teff, and millet
Foods to Avoid
Limiting or avoiding high-histamine foods or items that promote histamine release is another tactic to manage symptoms of histamine intolerance and reduced DAO activity.
Examples of foods with high histamine content or that can trigger histamine release include:
- alcoholic drinks like beer, wine, and spirits
- fermented foods such as sauerkraut, pickles, yogurt, and kimchi
- shellfish
- dairy products
- aged items like cheeses and smoked or cured meats
- wheat
- nuts, including peanuts and cashews
- certain fruits, such as citrus fruits, bananas, papaya, and strawberries
- certain vegetables, including tomatoes, spinach, eggplant, and avocado
- some food additives, colorings, and preservatives
Because low-histamine diets can be restrictive, they may increase the risk of nutrient shortfalls and reduce quality of life (1).
Therefore, strict low-histamine regimens should generally be temporary and used to identify specific food sensitivities.
Many people with histamine intolerance can tolerate limited quantities of high-histamine foods.
An elimination diet can help determine which foods provoke the most symptoms and should be avoided long-term versus those that can be consumed in moderation.
Ideally, this process is carried out under the supervision of a qualified healthcare professional to avoid complications.
SummaryNutritional strategies to support DAO function and reduce histamine exposure include elimination diet protocols and ensuring adequate intake of nutrients known to support DAO activity.
Safety Precautions and Dosage Recommendations
No adverse effects have been reported in studies examining DAO supplements.
However, because evidence remains limited, there is no universally accepted dosing guideline for DAO supplements.
Most studies administered 4.2 mg of DAO per dose, taken up to 2–3 times daily shortly before meals.
Consequently, comparable dosing appears safe for many individuals — but it is not completely without potential risk.
In countries like the United States, dietary supplements are not tightly regulated. It’s wise to choose products that have undergone third-party testing for purity and quality, such as certification by the U.S. Pharmacopeia (USP).
Always talk with your healthcare provider before beginning any new supplement.
SummaryDoses of 4.2 mg of DAO taken 2–3 times daily before meals have been studied without reported adverse reactions, though an established consensus on DAO dosing is still lacking.
The Bottom Line
DAO supplements do not cure histamine intolerance or DAO deficiency but may help relieve symptoms by breaking down external sources of histamine found in foods and drinks.
Further research is required to clarify their efficacy, safety, and optimal dosing, although existing studies have not reported adverse effects.
Be sure to consult with a qualified healthcare professional before adding any new supplement or medication to your health regimen.





















Leave a Reply
You must be logged in to post a comment.