A gum laceration will often mend on its own with simple home care like saltwater rinses and cold packs, though some situations may need professional medical care.
Mouth traumas are frequent, particularly in children and people prone to falls or those who play contact sports. While gum cuts are not as common as other oral injuries, they do occur.
Knowing how to quickly manage a cut on the gums at home aids healing and lowers the risk of infection. It’s also useful to recognize when to get medical help.
Read on to find out how to treat a gum cut and when to contact a healthcare professional.
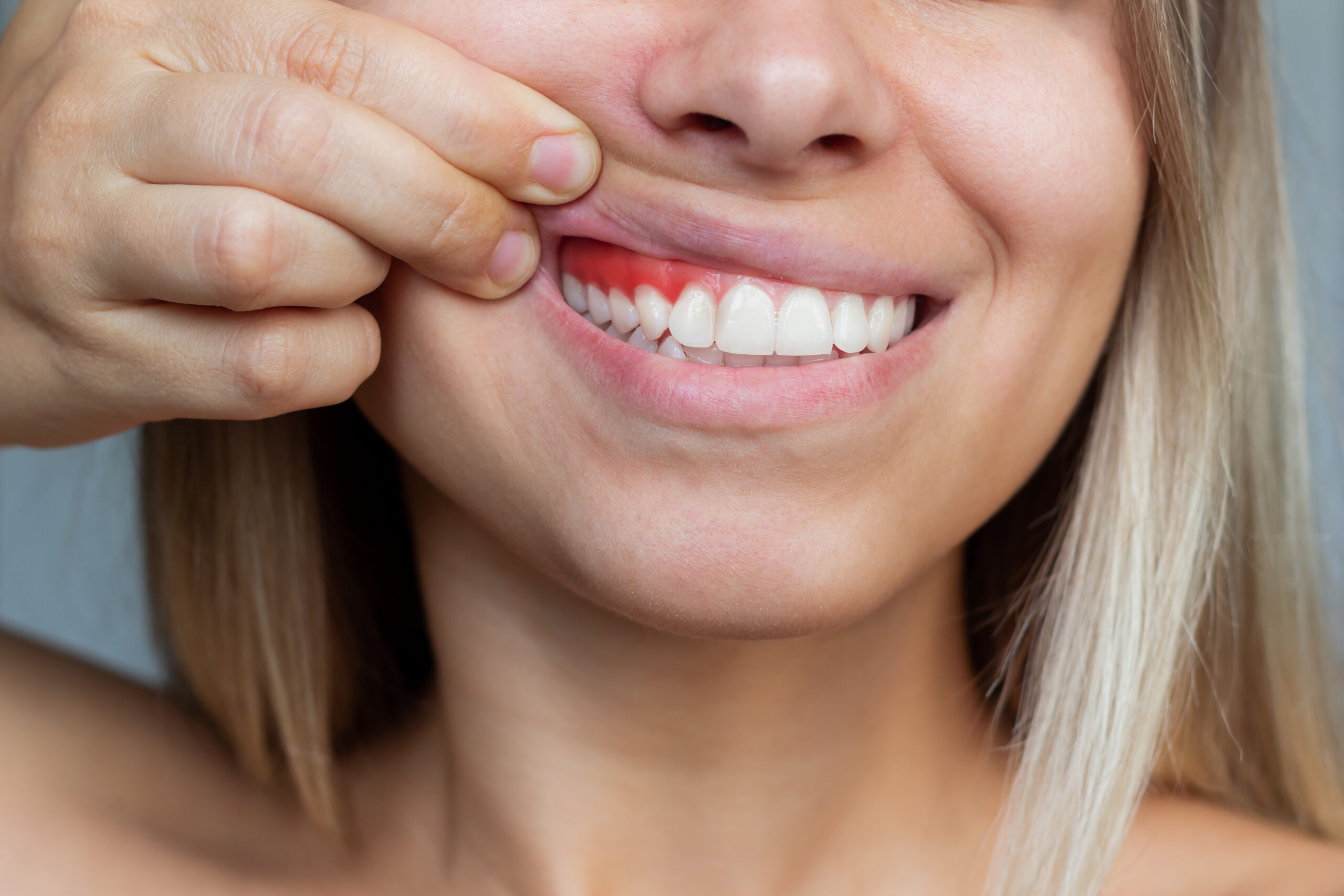

Where cuts can occur
You might get cuts on the outer areas of your mouth or face. Similar injuries can happen inside the mouth, along the gum tissue above your teeth.
Common causes include:
- a fall
- a sports-related impact
- placing sharp objects in the mouth
Gum cuts can also appear between teeth. These are less often due to trauma like falls and more commonly result from:
- incorrect flossing technique
- using toothbrushes with very stiff bristles
- using items such as toothpicks
How they look
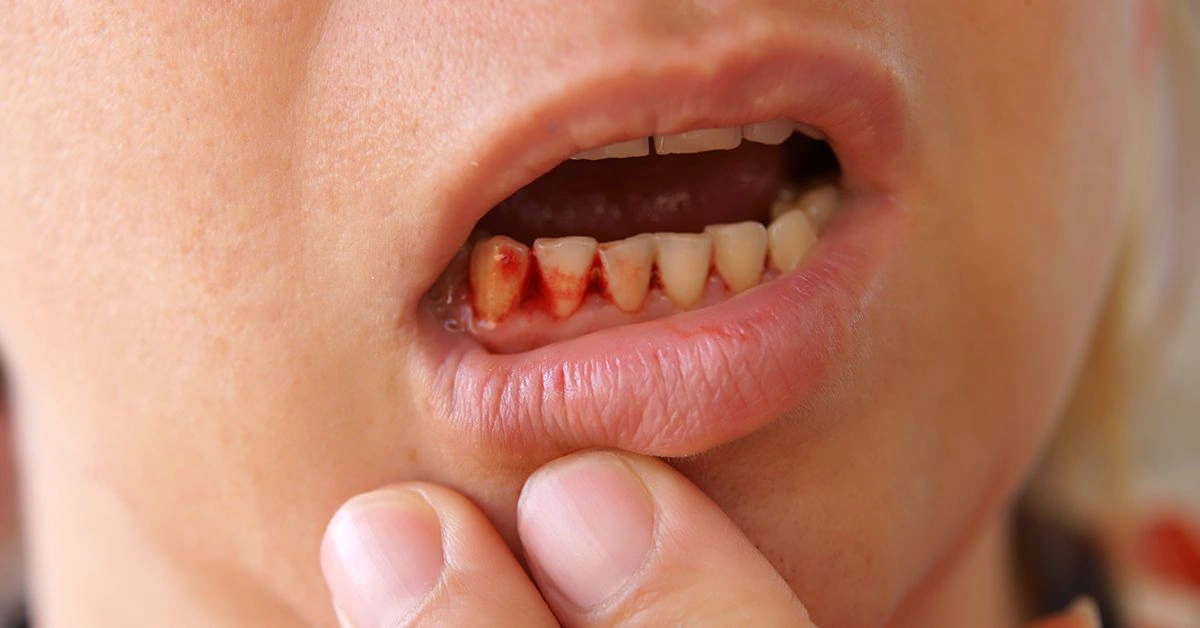
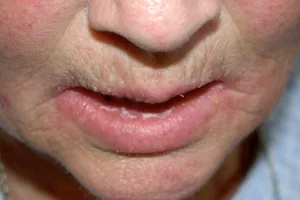
Gum cuts may bleed profusely because the gums have a rich blood supply, similar to the tongue and lips.
Besides bleeding and torn gum tissue, you might notice other changes in gum appearance, such as differences in color or texture. Watch for signs of infection as well.
Gum color
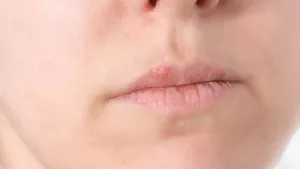
Initially, a gum cut may cause redness and swelling. As healing progresses, the area may turn temporarily white.
It’s common for oral wounds to develop a white appearance. This is a normal reaction to injury and usually resolves in a few days.
Swelling
After an injury, your gums may swell, appearing larger than before. The swollen area can look red and feel tender or sore.
Infections
Possible signs of infection include:
- fever
- chills
- pus discharge from the cut
- red streaks radiating from the wound
- worsening oral pain
- increased swelling of the affected gum
Treatment
Although a cut on the gums can be alarming, many are mild and can be managed at home.

Home remedies
- Control the bleeding. Gently press a clean cloth or paper towel against the gum for 5 to 10 minutes to help stop the bleeding. You can also rinse your mouth with cool water to clear away any debris.
- Use a salt rinse. This helps keep the area clean to reduce infection risk. Mix 1 teaspoon of salt into 1 cup of warm water and swish for several seconds. Repeat throughout the day as needed, particularly after eating.
- Adjust your diet. Temporary dietary changes may reduce discomfort and support healing. Eat soft foods and avoid hot, spicy, or citrus items. Sucking on ice chips or popsicles can help ease swelling.
- Apply a cool compress. You can place a cool, damp cloth against the injured area. Run a soft towel under cold water and hold it on the site for up to 20 minutes.
- Consider medication. Over-the-counter pain relievers may help with mild pain from gum cuts. Options include ibuprofen (Advil) or acetaminophen (Tylenol). Check with your doctor before using OTC drugs and follow dosing directions.
Medical care
Although rare for gum injuries, deep cuts that do not stop bleeding may need stitches. These sutures might be absorbable or may have to be removed by a dentist or physician within about a week.
Infected gum lacerations may require oral antibiotics.
A clinician will prescribe a course of antibiotics, typically lasting at least 7 days. It’s essential to complete the full course even if symptoms improve.
Healing time
Gums are delicate and prone to bleeding, but they also tend to heal quickly. A minor gum cut usually heals within 3 to 4 days.
Healing may take longer for larger cuts that need sutures or if the wound becomes infected.
When to get medical help
Generally, see a healthcare provider if a gum cut isn’t improving within a couple of days.
Even with treatment, a gum cut can become infected. Seek care promptly for an infection before it spreads.
A mild infection might be managed with oral antibiotics at home, whereas severe cases could require hospitalization.
Get medical attention right away if the gum cut keeps bleeding or if it initially improves but then worsens. Bleeding that does not stop after 10 minutes of pressure is an emergency.
Other warning signs that need urgent care include:
- trouble breathing
- difficulty swallowing fluids or food
- gum swelling or pain preventing you from closing your mouth
If your gums bleed without any cuts or other symptoms like pain, consult your dentist to rule out periodontal disease (gum disease).
Often caused by prolonged inadequate oral hygiene, gum disease may present with:
- bleeding gums, especially after brushing or flossing
- receding gumline
- red gums
- swollen gums
- bad breath
- loose teeth
- changes in your bite
With timely care, gum disease can be reversible.
Contact a dentist if you suspect a tooth injury that accompanies bleeding gums, with or without visible cuts.
The takeaway
Gum cuts can arise from sharp or hard items in the mouth or from falls and other injuries. Most are minor and resolve with home care.
If you notice new or worsening signs — such as severe pain, ongoing bleeding, or pus — consult a healthcare professional for treatment.
















Leave a Reply
You must be logged in to post a comment.