Itching (pruritus) can be more than a minor nuisance. It often causes notable discomfort and can become a distraction. You might be asking how to tell when itching requires attention and what home treatments can ease your itch.
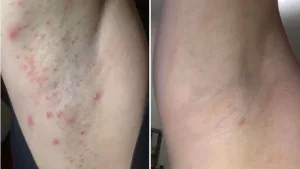
There are many reasons your skin may itch. You could have contacted an irritating plant, such as ragweed or poison ivy. Conditions like psoriasis and eczema often produce dry, itchy skin. Illness, insect bites, or the healing process after a burn or cut can also trigger itchiness.
Keep reading to discover effective remedies for itchy skin and guidance on when to consult a healthcare professional.

Anti-itch creams
Anti-itch creams are a common way to calm itchy skin. Consider trying a product that contains hydrocortisone. This medication suppresses inflammatory reactions and can help soothe inflamed, itchy areas.
If over-the-counter (OTC) options don’t provide relief, your physician might prescribe a stronger corticosteroid cream to lower inflammation. By addressing the underlying inflammation in certain skin disorders, like eczema, you may find relief from itching.
Hydrocortisone and corticosteroid creams should be used for the briefest period necessary (generally 1 to 2 weeks) before stopping. Prolonged use can cause side effects such as skin thinning and potential dependence. Avoid applying hydrocortisone creams to the face unless advised by a doctor.
Applying topical antihistamines straight to the irritated skin may be preferable to taking oral antihistamines because oral versions can have systemic side effects.
Examples of anti-itch creams include Cortisone-10 and topical Benadryl.
Colloidal oatmeal
Colloidal oatmeal isn’t for eating. It’s made by grinding oats into a very fine powder. Many manufacturers include this natural ingredient in soaps and lotions, and you can add it to a cool bath.
One study found that colloidal oatmeal is safe and helps relieve itch and moisture loss while supporting the skin barrier.
Another trial revealed that adding 1% colloidal oatmeal to a topical cream improved skin. Of 61 participants, 30 used the 1% colloidal oat eczema cream, while 31 used a standard moisturizer.
The results showed the group using the 1% colloidal oat cream had notable gains in skin barrier function, hydration, and pH balance. The standard moisturizer group showed improvement only in hydration.
You can purchase colloidal oatmeal at many pharmacies or make your own by grinding oats into a fine powder.
Leaf gels
Consider plant-based options like aloe vera gel, which helps skin retain moisture, or provides relief for mild itches from sunburns or insect bites.
Menthol, which gives a cooling sensation, comes from the peppermint plant. Use topical menthol carefully because it can irritate the skin if not properly diluted. Both aloe vera and menthol products are available at most drugstores.
High quality moisturizers
Good moisturizers lock water into the outer layer of your skin. This helps your skin feel more hydrated and less dry and itchy. For better absorption, apply them to damp skin, such as right after bathing.
Different moisturizers address different causes of dryness. Some, like those with beeswax, coconut oil, or mineral oil, create a barrier to prevent moisture loss. Others, such as glycerin-based products, aid in repairing the skin barrier.
Consult a dermatologist before selecting a moisturizer to determine which is best for your skin type.
Cold packs
A straightforward approach for quick itch relief is a cold pack or a bag of ice.
The essential factor is cold. Try to avoid exposing the itchy area to hot water, as heat can exacerbate the irritation.
Oral antihistamines
Histamines are chemicals that produce allergy symptoms, including itching.
Antihistamines are commonly used for allergic reactions, but many can cause drowsiness, so they are often best taken at night.
Oral antihistamines tend to be most effective when the itching is allergy-related. They may be less helpful for sudden itchiness from dry skin or other nonallergic causes.
Speak with your doctor before using any OTC oral antihistamines, particularly if you take other medications.
Petroleum jelly
If your skin is very dry and cracked along with being itchy, consider a petroleum jelly product like Vaseline or Aquaphor.
These products are gentle enough for facial use, including delicate areas such as eyelids and lips. However, avoid petroleum jelly on the face if you have oily skin, since it can cause breakouts.
Although petroleum jelly works best on damp skin, you can reapply it to dry skin during the day as needed.
Antidepressants
Some studies suggest certain antidepressants may help with itching. These medications can prompt serotonin release that relaxes receptors linked to the itch sensation.
This approach is usually reserved for more persistent cases of itching, and additional research is needed to confirm effectiveness.
Resist the urge to scratch
Scratching is a natural reaction to an itch, but it’s usually counterproductive. Scratching can damage the skin, hinder healing, and even lead to infection.
Try not to scratch. Wear comfortable, nonirritating clothing and keep your nails trimmed. Wearing cotton gloves at night may help prevent you from scratching while asleep.
Use fragrance-free lotions only
Your favorite body lotion might be worsening your itch due to added fragrances. Read product labels carefully and opt for items marked “fragrance-free” to reduce irritation. This is especially critical if you have eczema, psoriasis, or rosacea.
How to relieve itchy skin
Try the following steps to ease itchy skin quickly, using some of the remedies listed above:
1. Apply cool treatments
Use a cold compress or damp washcloth on small itchy spots caused by rashes, bug bites, or burns. Use this for 5 to 10 minutes at a time. For large areas, consider a cool bath instead.
2. Take an oatmeal bath for additional relief
For more extensive rashes, sunburn, or hives, try an oatmeal bath. Use lukewarm water and gradually add colloidal oatmeal, stirring occasionally so it doesn’t settle on the tub bottom.
Limit bathing time to 15 to 20 minutes.
3. Apply moisturizer to damp skin
After any cooling treatment or an oatmeal bath, immediately apply moisturizer. Damp skin absorbs lotions and emollients more effectively. If you’re using a medicated ointment, apply it before your moisturizer.
4. Consider combination therapies for chronic itchy skin
Depending on the cause, multiple treatments may be beneficial, especially for chronic itching.
For example, persistent itch from conditions like eczema might improve with colloidal oatmeal baths, topical emollients, and anti-itch creams.
Discuss combination therapies with your doctor before starting them.
Tips for relieving itchy skin
Making certain lifestyle adjustments can also ease itchy skin. Consider these tips:
- Wear loose clothing to avoid trapping moisture against your skin.
- Choose natural fabrics, such as cotton.
- Avoid sudden temperature extremes; keep your home cool in summer and humid in winter.
- Use lukewarm water for bathing and avoid hot tubs.
- Reduce stress whenever possible, as stress can worsen skin inflammation and itching.
- Use fragrance-free soaps, detergents, and lotions to minimize irritation.
When is itching a serious problem?
See your doctor if you have persistent itching for 3 or more days.
Although itchiness often isn’t serious, widespread itching can sometimes signal a more serious condition, such as thyroid, kidney, or liver disease, or even cancer. Talk with your physician if you’ve been itchy for 6 weeks or longer.
Contact your doctor right away if you experience severe itching without any bites, wounds, or visible rash.




















Leave a Reply
You must be logged in to post a comment.