Every year brings more choices for contraception. Different methods meet different needs and preferences, and each has distinct advantages and potential downsides depending on what you require.
Below is an overview of several birth control options available so you can visit your healthcare provider informed and ready to choose.
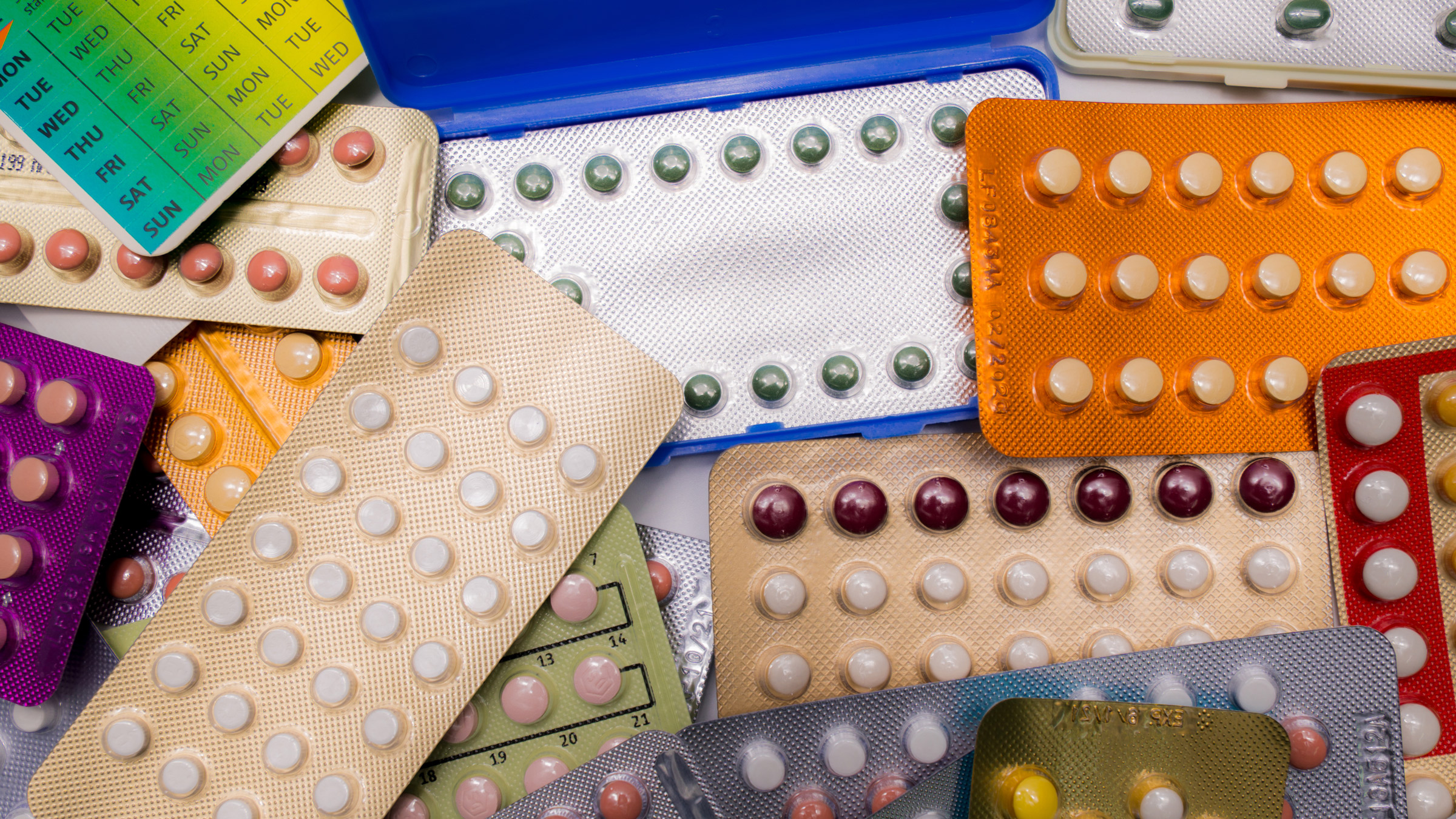
What are combination pills?
Combination pills include synthetic hormones called estrogen and progestin. They are formulated in various proportions and arrangements of active and inactive tablets.
When used correctly, the combination pill is over 99 percent effective.
Conventional pills
The most typical combination pill packs contain either 21 active tablets and 7 inactive tablets, or 24 active tablets and 4 inactive tablets. During the inactive tablet days, you may experience bleeding similar to a standard menstrual period.
Monophasic pills
Monophasic pills deliver a single, steady dose of hormones. Each active pill contains the same hormone level throughout the cycle.
Common monophasic brands in the United States include:
- Apri
- Alesse
- Aranelle
- Aviane
- Beyaz
- Desogen
- Estrostep Fe
- Gianvi
- Kariva
- Lessina
- Levlite
- Levora
- Loestrin
- Lybrel
- Lo Ovral
- Nordette
- Ocella
- Low-Ogestrel
- Ortho-Novum
- Previfem
- Reclipsen
- Safyral
- Velivet
- Yasmin
- Yaz
Multiphasic pills
Multiphasic pills vary the amount of active hormones depending on the stage of your cycle.
Biphasic pill brands include:
- Azurette
- Mircette
Triphasic pills include:
- Caziant
- Enpresse
- Ortho Tri-Cyclen
- TriNessa
- Velivet
Quadriphasic pills include:
- Natazia
Extended-cycle pills
If you prefer fewer monthly bleeds, a provider might recommend an extended-cycle or continuous-dose pill. These packs typically include 84 active tablets and 7 inactive tablets, resulting in roughly four periods a year.
Common extended-cycle brands include:
- Seasonale
- Seasonique
- Lybrel
Low-dose pills
Low-dose pills contain under 50 micrograms of estrogen per active tablet. They’re a good choice if you’re sensitive to hormones or tend to have side effects with standard pills, and they’re often recommended when initiating birth control.
While many do well on low-dose pills, these formulations can cause more breakthrough bleeding than higher-estrogen options.
Common low-dose brands include:
- Apri
- Aviane
- Levora
- Loestrin
- Lo Ovral
- Ortho-Novum
- Yasmin
- Yaz
Considering changing pill brands? Here’s a guide to switching birth control pills.
What are minipills?
Minipills are formulated with progestin only and contain no estrogen. This makes them suitable for people with certain health conditions or sensitivities to estrogen.
Each minipill contains the same active hormone dose and there are no placebo tablets. You might have menstrual bleeding or skip a period while using this method. The progestin dose in minipills is lower than the progestin amount found in combination pills.
When taken properly, minipills are also over 99 percent effective. They have a narrow 3-hour dosing window, so clinicians advise taking them at the same time every day.
Common minipill brands include:
- Camila
- Errin
- Heather
- Jencycla
- Jolivette
- Nor-QD
- Nora-BE
- Orthoa Micronor
How are combination pills and minipills different?
The principal distinction is that combination pills include estrogen while minipills do not. They also work differently within the body.
Combination pills reduce pregnancy risk via three mechanisms. First, the hormones stop the ovaries from releasing an egg. Without ovulation, sperm have nothing to fertilize.
These hormones also cause the cervical mucus to thicken and become sticky, which inhibits sperm passage through the cervix. Some combination formulations also thin the uterine lining, making implantation of a fertilized egg less likely.
Minipills primarily prevent pregnancy by thickening cervical mucus and thinning the uterine lining. Certain progestin-only pills can also suppress ovulation, but that is not their primary action.
What are the side effects of birth control pills?
Many individuals tolerate birth control pills well with no symptoms. However, some people experience unwanted effects, particularly when starting a new pill.
Potential side effects of combination pills include:
- nausea
- vomiting
- headache
- weight gain, often from fluid retention
- breast tenderness
- spotting between periods
- cramping
Possible side effects of progestin-only minipills include:
- acne
- breast tenderness
- headache
- fatigue
- spotting between periods
- ovarian cysts
- weight gain
- reduced libido
Worried about cramps? Learn how birth control pills can affect cramping.
What causes birth control pill side effects?
Pills contain hormones intended to maintain consistent hormone levels across your cycle. This steadiness helps prevent ovulation and lowers pregnancy risk.
Side effects may stem from shifts in hormone levels, which can happen when you start a pill, delay a dose, or miss one entirely.
Most side effects diminish within several weeks to months of continuous use. If symptoms persist after about 3 months, consult your provider — you may need an alternative method.
Want more detail? Here are the pros and cons of hormonal versus nonhormonal contraception.
Risk factors to consider when taking birth control
For many people, birth control is safe and effective. Certain health factors can increase the chance of adverse effects.
Discuss your medical history with a clinician before starting contraception to determine whether any medications or methods should be avoided.
You may face higher risk of complications if you:
- are older than 35 and smoke
- have a personal history of breast cancer
- have high blood pressure
- have had a heart attack or have heart disease
- have a history of stroke
- have blood clotting disorders
- have had diabetes for more than 10 years
If you are breastfeeding, you may need to postpone certain contraceptives until you stop nursing. The progestin-only minipill may be suitable for some people who are breastfeeding; discuss options with your clinician.
Birth control brands comparison chart
Brand nameGeneric nameTypeSchedule (active/inactive)Alesselevonorgestrel and ethinyl estradiolmonophasic21 days/7 daysApridesogestrel and ethinyl estradiollow-dose monophasic21 days/7 daysSafyraldrospirenone/ethinyl estradiol/levomefolate calcium and levomefolatemonophasic21 days/7 daysLo Loestrin FEnorethindrone acetate and ethinyl estradiollow-dose monophasic26 days/2 daysSeasoniquelevonorgestrel and ethinyl estradiolextended cycle84 days/7 daysCamilanorethindroneminipill28 daysYazdrospirenone and ethinyl estradiollow-dose monophasic24 days/4 daysYasmindrospirenone and ethinyl estradiollow-dose monophasic21 days/7 daysEnpresselevonorgestrel and ethinyl estradioltriphasic21 days/7 daysAzurettedesogestrel/ethinyl estradiol and ethinyl estradiolbiphasic21 days/7 days
Optum Perks is owned by RVO Health. By clicking this link, we may earn a commission. Learn more.
How to choose a birth control pill
Consult a clinician when choosing between pill types. All are effective, but choices may be influenced by your medical background, lifestyle, and desired outcomes.
Before your appointment, think about whether you prefer a combination pill containing estrogen or a progestin-only minipill.
Minipills are useful if you cannot take estrogen. Consider whether having fewer or no regular periods matters to you, since minipills can affect bleeding patterns.
Evaluate the benefits and drawbacks of each pill category. After you select a pill type, your provider might suggest specific brands. Remember that what works for one person may not work for another.
It’s common to try different pill types or doses before finding the best fit.
Whether you pick a combination pill or a minipill, allow time to adapt and monitor how your body responds. Most providers advise staying on a particular pill for about 3 months before switching.
Notify your clinician if side effects interfere with daily life or become troublesome. They may suggest trying a different pill.
No time for the pharmacy? Here’s how to get birth control pills online.
Frequently asked questions about birth control pills
What’s the most common birth control pill?
The combination pill and the minipill are the two most frequently used oral contraceptives.
What’s the cheapest birth control pill brand?
Costs vary. In the United States, you should be able to obtain free or low-cost birth control in many locations. See our guide for more details.
Do I need to contact a doctor to get birth control pills?
Generally, yes. Most birth control pills require a prescription from a doctor, nurse, or Planned Parenthood. Some states allow prescriptions online or from pharmacists. Opill, a progestin-only pill, is available over the counter without a prescription in some places.
Where can I get birth control pills?
With a prescription, you can obtain birth control pills at a pharmacy or via online services.
Takeaway
Combination pills and minipills are the most common oral contraceptives. Choosing between them depends on factors such as whether you prefer a pill that includes estrogen or one that does not.
Side effects, costs, and individual responses vary. Discussing options with a healthcare provider can help you identify the pill that best fits your needs.























Leave a Reply
You must be logged in to post a comment.