Studies indicate that apple cider vinegar might offer certain health advantages, such as antimicrobial and antioxidant actions.
Apple cider vinegar is a well-known folk remedy. It has been used for generations in cooking and traditional medicine, and it may provide some health improvements.
Possible benefits include:
- supporting weight reduction
- lowering cholesterol
- reducing blood glucose levels
- easing symptoms associated with diabetes
Nonetheless, only a limited amount of research is available, and additional studies are required before it can be routinely recommended as an alternative treatment.
This piece reviews the evidence behind six potential health advantages of apple cider vinegar.

1. Rich in acetic acid
Acetic acid is the main active ingredient in vinegar, responsible for its sharp sour scent and taste. Researchers attribute many of apple cider vinegar’s effects to this acid. Cider vinegars typically contain about acetic acid.
It also contains a component known as “mother,” a mesh of proteins, enzymes, and friendly bacteria that gives the liquid a cloudy look.
Some people claim the mother accounts for much of the health value, although no studies have confirmed this.
While apple cider vinegar is not a significant source of vitamins or minerals, high-quality brands may provide small amounts of amino acids and antioxidants.
2. Can help eliminate harmful microbes
Vinegar can assist in killing pathogens, including various bacteria.
Traditionally, vinegar has been used for cleaning and disinfecting, as well as treating nail fungus, lice, warts, and ear infections.
Hippocrates, often called the father of medicine, used vinegar to cleanse wounds over 2,000 years ago.
Vinegar also serves as a food preservative. Research shows it can prevent bacteria like E. coli from growing and spoiling foods.
If you want a natural method to preserve food, apple cider vinegar may be useful.
3. May help reduce blood sugar and support diabetes management
So far, one of the most promising uses of vinegar is in helping manage type 2 diabetes.
Type 2 diabetes involves elevated blood sugar due to insulin resistance or inadequate insulin production.
Even people without diabetes might benefit from maintaining blood sugar within normal ranges, as some researchers suggest chronic high blood sugar contributes to aging and various long-term diseases.
A clinical trial suggests that consuming apple vinegar may positively affect the glycemic index and oxidative stress in people with diabetes and dyslipidemia. Another trial found that ACV intake may improve glycemic markers in adults.
However, these results should be treated cautiously because larger, more rigorous studies are necessary to clarify apple cider vinegar’s potential effects. Indeed, health authorities advise against substituting proven medical treatments with unverified remedies.
Apple cider vinegar is generally considered safe. If you take medications that lower blood sugar, consult your physician before increasing your vinegar intake.
4. May support weight loss
Somewhat surprisingly, research indicates vinegar could help with weight loss.
Multiple human studies show vinegar can boost feelings of fullness, which may lead to reduced calorie intake and weight loss.
One review noted that in short-term trials where participants consumed apple cider vinegar with solid-food meals, they experienced appetite suppression for up to 120 minutes after eating and tended to snack less afterward.
However, longer-term studies in the review did not show a clear link between apple cider vinegar and sustained appetite suppression.
That said, a 2024 randomized controlled trial reported notable reductions in weight (6–8 kg), body fat percentage, waist and hip measurements, BMI, blood glucose, and blood lipids after daily intake of three doses of apple cider vinegar (15 milliliters per tablespoon) for 12 weeks. Larger trials are needed to confirm these outcomes.
5. May benefit heart health
Cardiovascular disease remains one of the leading causes of death.
Several biological factors influence heart disease risk.
Research suggests vinegar might improve some of these factors, but many studies on apple cider vinegar’s cardiovascular effects were performed in animals and may not translate directly to humans.
A review of studies in both humans and animals observed that apple cider vinegar could potentially improve levels of high-density lipoprotein, low-density lipoprotein, triglycerides, and total cholesterol.
Another review of human research found that apple cider vinegar may have a favorable effect on total cholesterol.
However, both reviews highlighted limitations in study quality and sample size, so more research is necessary before drawing firm conclusions.
6. May enhance skin health
Some people apply apple cider vinegar as a home remedy for skin issues like dry skin and eczema.
Skin is naturally slightly acidic, but in people with eczema it can be less acidic. Applying diluted apple cider vinegar topically may help restore the skin’s pH and strengthen its protective barrier.
However, evidence is mixed, and some experts warn that apple cider vinegar can irritate skin in certain individuals, particularly those with sensitive skin.
Consult a healthcare provider before trying new treatments, especially on damaged skin. Do not apply undiluted vinegar to the skin, as it can cause burns.
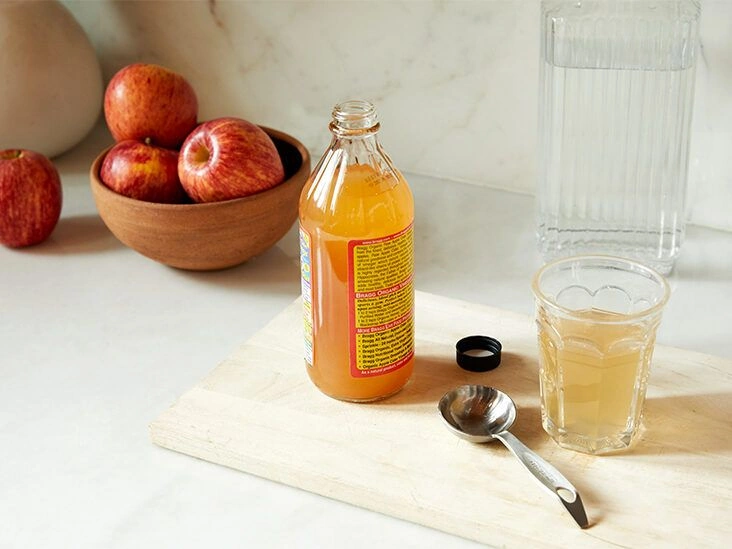
Dosage and how to use it
The simplest way to add apple cider vinegar to your diet is through cooking. It works well in salad dressings and homemade mayonnaise.
Some people dilute it in water and drink it. Typical amounts range from 1–2 teaspoons (5–10 mL) to 1–2 tablespoons (15–30 mL) per day mixed into a large glass of water.
Begin with small amounts and avoid excessive intake. Too much vinegar can have adverse effects, such as tooth enamel erosion and potential interactions with medications.
Some nutritionists suggest choosing organic, unfiltered apple cider vinegar that contains “mother.”
Read more about appropriate apple cider vinegar dosages here.
Frequently asked questions
What are the drawbacks of apple cider vinegar?
Using apple cider vinegar can cause some side effects, including:
- possible indigestion
- potentially lower potassium levels
- erosion of tooth enamel
- skin and throat burns
- interactions with certain drugs, such as diuretics and some diabetes medications
That said, a common daily dose of 1–2 tablespoons is unlikely to produce these effects for most people.
Is it better to drink apple cider vinegar in the morning or at night?
Although apple cider vinegar may offer some benefits, there’s limited research comparing consumption before bed versus other times like the morning. To prevent issues such as indigestion or acid reflux at night, avoid consuming it within at least before bedtime.
Learn more: Should you drink apple cider vinegar before bed?
What are the advantages of apple cider vinegar gummies?
Gummies containing apple cider vinegar may provide similar small benefits to consuming a little vinegar, such as potential effects on cholesterol and blood sugar. They often include additional vitamins or minerals.
However, there’s no definitive proof that gummies are equivalent to liquid vinegar, and some gummies contain added sugar, which could counteract benefits for blood sugar control.
Learn more: Are there benefits to apple cider vinegar gummies?
The bottom line
Many websites and natural health advocates assert that apple cider vinegar delivers remarkable health benefits, including boosting energy and treating illness.
Unfortunately, strong evidence supporting most of these claims is lacking.
Still, some studies suggest apple cider vinegar may have certain effects, such as killing bacteria, lowering blood sugar, and aiding modest weight loss.
Apple cider vinegar appears safe when diluted and used in moderation.
It also has a variety of non-health uses, such as a natural hair rinse, skin care adjunct, and household cleaner.
Read this article in Spanish





















Leave a Reply
You must be logged in to post a comment.