Ever wondered exactly what a heart specialist does all day? In a nutshell, cardiologists blend detective work, high‑tech testing, thoughtful treatment planning, and a lot of genuine care. They listen to your story, run the right scans, decide whether medication, a procedure, or lifestyle tweaks are best, and then stick with you through follow‑ups. Knowing these duties helps you know when to call one, what to expect during a visit, and how to partner with them for a healthier ticker.
Core Duties
At the heart of every cardiologist’s job is a set of core duties that keep patients’ circulatory systems running smoothly. Below is a quick‑look table that breaks them down.
| Duty | What It Looks Like in Practice |
|---|---|
| Patient Consultation & History‑Taking | Chatting with you about symptoms, family history, lifestyle, and worries – often the first clue to a heart issue. |
| Diagnostic Test Ordering & Performance | Scheduling ECGs, echocardiograms, stress tests, cardiac MRI/CT scans, or cardiac catheterisations. |
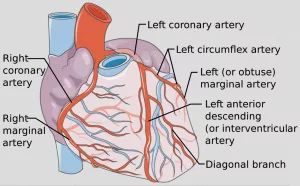
| Result Interpretation & Diagnosis | Reviewing images and data, then pinpointing conditions such as arrhythmia, valve disease or coronary artery blockage. |
| Treatment Planning | Choosing meds, recommending diet/exercise, or arranging a procedure; always tailored to you. |
| Procedural Involvement | Performing or assisting with catheterisations, angioplasties, pacemaker insertions, or other minimally invasive interventions. |
| Long‑Term Management & Education | Scheduling follow‑ups, adjusting therapies, teaching you how to read your own blood pressure or manage cholesterol. |
| Team Collaboration & Training | Coordinating with surgeons, nurses, and teaching residents – the heart team works hand‑in‑hand. |
Let’s walk through each of those duties with a little more colour.
Consultation & History‑Taking
Imagine walking into a cozy exam room and the cardiologist greets you with a smile, then asks “When did you first notice that tightness in your chest?” That simple question opens a door to a deep dive: your family’s heart‑health history, smoking habits, stress levels, even your sleep patterns. A real‑world example: Maria, a 48‑year‑old marketing director, thought her occasional shortness of breath was just “getting older.” After a thorough conversation, her doctor caught early‑stage atrial fibrillation and got her on the right rhythm‑control meds before things got scary.
Diagnostic Tests
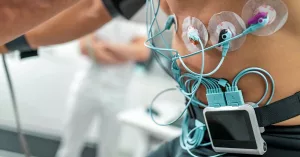
Most of the time, cardiologists are also technologists. They’ll order an electrocardiogram (ECG) to capture your heart’s electrical rhythm, or an echocardiogram that uses sound waves to watch the heart pump in real time. Stress tests reveal how your heart behaves under exertion, while cardiac MRI or CT scans provide a 3‑D map of arteries and valves. According to BetterTeam, these tests are the bread and butter of a cardiologist’s diagnostic toolkit.
Interpreting Results
Once the data rolls in, the cardiologist becomes a forensic analyst. A subtle ST‑segment shift on an ECG might hint at silent ischemia; a slightly thickened left ventricle on an echo could flag early heart‑failure. They compare numbers to guidelines from the American College of Cardiology (ACC) and the American Heart Association (AHA) – the gold standards that keep practices evidence‑based.
Developing Treatment Plans
After the mystery is solved, the next chapter is treatment. This could be as simple as prescribing a beta‑blocker and suggesting a low‑sodium diet, or as complex as planning a cardiac catheterisation to open a blocked artery. Most cardiologists balance medication with lifestyle tweaks, because a healthy heart is part lifestyle, part science. They’ll often hand you a printable “Heart‑Healthy Checklist” that includes steps like “walk briskly 30 minutes a day” or “swap sugary drinks for water.”
Procedural Involvement
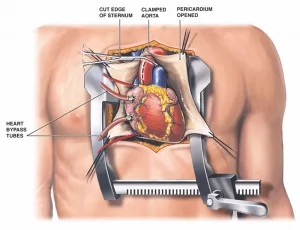
While many cardiologists focus on non‑surgical care, a good number perform minimally invasive procedures. Cardiac catheterisation, for instance, threads a thin tube through a blood vessel to the heart, allowing doctors to measure pressures and inject contrast dye for clear images. In some cases, they’ll balloon‑dilate a narrowed artery (angioplasty) or place a stent to keep it open. According to Prospects, these interventions are cornerstone services in modern cardiology.
Long‑Term Management & Education
Heart disease rarely resolves after one visit. Cardiologists stay involved with regular check‑ups, tweaking meds, monitoring lab results, and cheering you on when you hit a new step‑count record. They might suggest a cardiac rehabilitation program—a blend of supervised exercise, nutrition advice, and emotional support—that dramatically reduces the risk of future events.
Team Collaboration & Training
Heart care is a team sport. Cardiologists work side‑by‑side with cardiac surgeons, electrophysiologists, nurses, dietitians, and even mental‑health counselors. In teaching hospitals, they also mentor residents and fellows, passing on the craft of listening to a patient’s pulse—both literally and figuratively.
Specialized Roles
Not every cardiologist does the same thing. After mastering the basics, many drill down into sub‑specialties that focus on particular patient groups or procedures.
Interventional Cardiology
These doctors are the “hands‑on” experts who perform catheter‑based procedures like angioplasty, stent placement, and sometimes complex valve repairs. Their daily rhythm involves the cath lab, fluoroscopy screens, and a whole lot of precise hand‑eye coordination.
Electrophysiology
Think of these specialists as the DJs of heart rhythm. They diagnose arrhythmias, implant pacemakers or defibrillators, and run sophisticated studies that map the heart’s electrical pathways.
Cardiac Imaging
Imaging cardiologists become visual storytellers. They interpret echocardiograms, cardiac MRIs, CT scans, and nuclear images, turning patterns of pixels into actionable diagnoses.
Heart Failure & Transplant
These physicians manage patients with advanced heart disease, often coordinating with transplant teams, LVAD (left ventricular assist device) programs, and palliative‑care services.
Pediatric Cardiology
While most cardiologists treat adults, pediatric cardiologists focus on newborns, children, and teens. Congenital heart defects, childhood arrhythmias, and growth‑related valve issues are their playground.
Benefits & Risks
Understanding both the upside and the potential downsides of cardiologist responsibilities can help you feel empowered when you step into the clinic.
Benefits for Patients
- Early detection: Routine check‑ups and screenings can catch silent disease before it becomes life‑threatening.
- Targeted treatment: Precise diagnostics lead to therapies that work and minimize side‑effects.
- Holistic support: Lifestyle coaching from a heart specialist often leads to lasting habit change.
Potential Risks / Pitfalls
- Over‑testing: Unnecessary radiation exposure or false‑positive results can cause anxiety.
- Medication interactions: Heart drugs can clash with other prescriptions; careful review is essential.
- Procedural complications: Even minimally invasive procedures carry a small risk of bleeding or vessel injury.
How Cardiologists Mitigate Risks
Top‑tier cardiologists lean on evidence‑based guidelines, shared decision‑making, and continuous quality‑control. They’ll walk you through the pros and cons of each test or treatment, make sure your medication list is up‑to‑date, and only recommend procedures when the benefit clearly outweighs the risk.
Day In The Life
Curious about what a typical day looks like? Here’s a friendly timeline that paints the picture (exact schedules vary by practice).
| Time | Activity |
|---|---|
| 07:30 – Morning Huddle | Review overnight alerts, assign cases, coordinate with the cath lab team. |
| 08:30 – First Consults | Meet patients, take histories, perform quick physical exams. |
| 10:00 – Imaging Review | Read echocardiograms, discuss CT scans with radiology. |
| 12:00 – Lunch & Case Review | Multidisciplinary board round‑table for complex cases. |
| 13:30 – Procedural Block | Cardiac catheterisation or pacemaker implantation in the lab. |
| 16:00 – Follow‑Up Calls | Adjust meds, answer patient questions, provide reassurance. |
| 18:00 – Documentation & Teaching | Log notes, mentor residents, update care plans. |
Whether you’re in a bustling hospital or a quiet private clinic, the rhythm is a blend of patient interaction, data analysis, and procedural focus.
Choosing The Right Cardiologist
Now that you know what they do, how do you pick the right heart specialist for you? Here’s a quick checklist you can use during your search.
| Factor | What To Look For |
|---|---|
| Credentials | Board‑certified in cardiology, fellowship training, hospital affiliations. |
| Experience With Your Condition | Ask about specific cases like atrial fibrillation, heart failure, or valve disease. |
| Communication Style | Do they explain things in plain language? Are they empathetic? |
| Patient Outcomes & Reviews | Look for reputable sources—hospital quality rankings, peer‑reviewed outcomes. |
| Accessibility | Office hours, emergency contact options, tele‑cardiology availability. |
If a doctor ticks most of those boxes, you’re likely in good hands. Remember, a great partnership is a two‑way street—your questions and their answers both matter.
Future Trends Shaping Responsibilities
The world of cardiology is evolving fast, and today’s responsibilities are already shifting toward new technology and care models.
Artificial Intelligence & Imaging
AI algorithms can flag subtle changes on an echocardiogram that the human eye might miss. Early studies show a 15‑20% boost in diagnostic accuracy, meaning cardiologists will spend less time hunting for clues and more time planning care.
Tele‑Cardiology & Remote Monitoring
Wearable devices now stream heart‑rate variability, rhythm, and even blood‑pressure data straight to a doctor’s dashboard. This lets cardiologists monitor patients between visits, catching issues before they flare.
Precision Medicine
Genetic testing is uncovering why certain patients respond better to specific drugs. In the near future, a cardiologist may prescribe a medication tailored to your DNA profile, reducing side‑effects and improving outcomes.
Value‑Based Care
Hospitals are moving from fee‑for‑service to value‑based reimbursement, which rewards outcomes over volume. That pushes cardiologists to focus even more on preventive strategies, patient education, and coordinated care pathways.
All these trends mean the card‑i‑o‑logist’s role will keep expanding—more data, more collaboration, and still the same compassionate bedside manner.
Conclusion
Cardiologist responsibilities span listening, diagnosing, treating, and teaching. From the first “How are you feeling today?” to the final follow‑up call months later, they act as detectives, technicians, surgeons, and lifelong mentors. Understanding their core duties, specializations, and the balance of benefits and risks empowers you to make informed choices about your heart health.
If you’ve ever felt uncertain about when to see a heart specialist or what to expect during a visit, I hope this guide clears the fog. Feel free to share your own experiences, ask questions in the comments, or simply reach out to a local cardiology clinic for a friendly chat. After all, a healthier heart is a happier life—let’s keep it beating strong together.

















Leave a Reply
You must be logged in to post a comment.