Because of its antioxidant and anti-inflammatory components, sesame oil may support heart health, ease joint issues, benefit the skin and hair, and more. However, additional research — particularly human trials — is required to confirm these possible advantages.
The nourishing qualities of the sesame plant have led some to call its oil the “Queen of Oilseeds”.
Part of the Pedaliaceae family, a group of plants harvested for their edible seeds, its scientific name is Sesamum indicum.
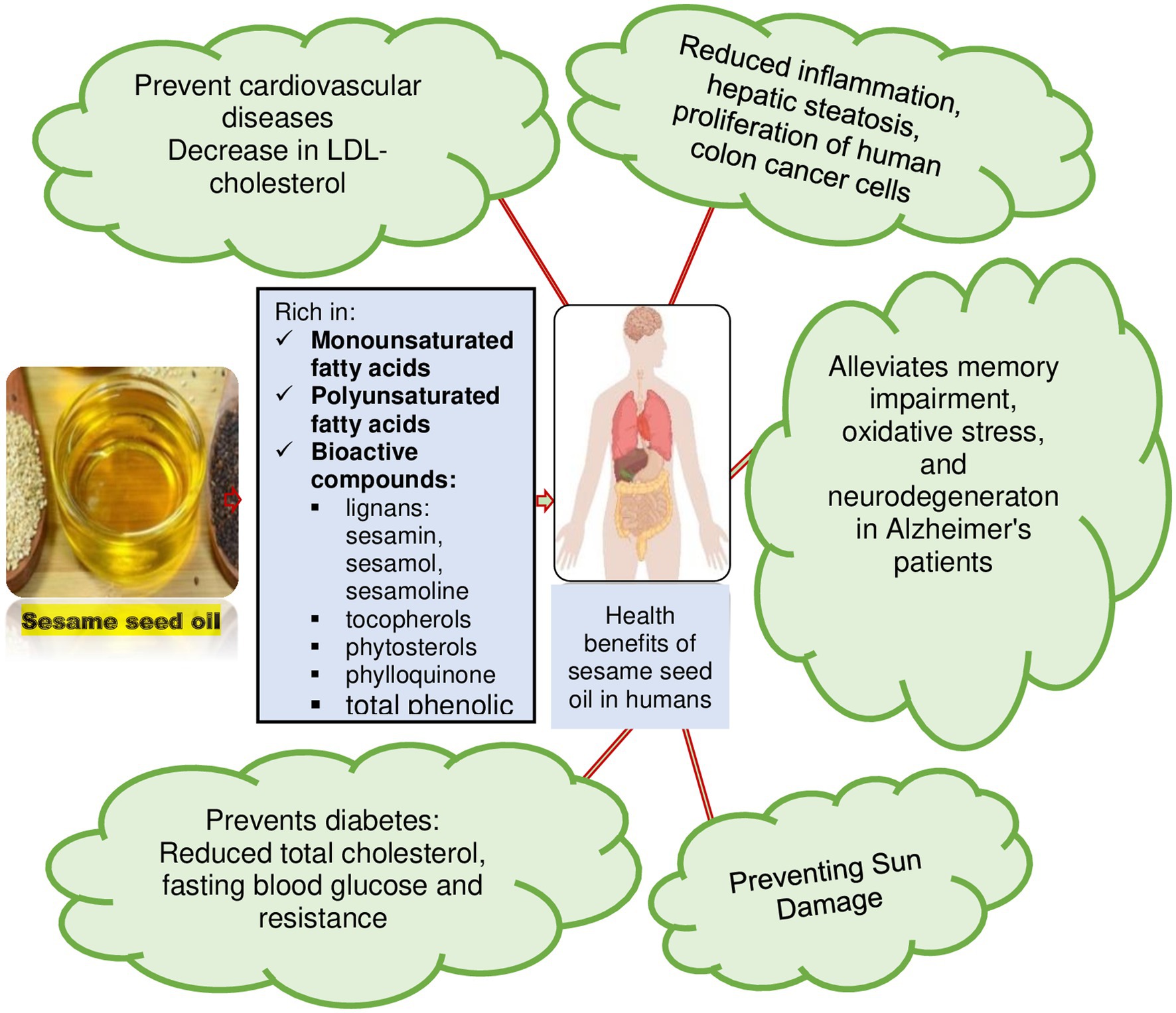
Sesame oil is extracted from pressed sesame seeds and is used for culinary, medicinal, and cosmetic purposes.
This article summarizes 10 scientifically supported benefits of sesame oil.
1. Packed with antioxidants
Sesame oil contains sesamol and sesaminol, antioxidants that may provide notable health advantages.
Antioxidants help limit cellular damage from free radicals. When free radicals build up in cells, they can contribute to inflammation and disease.
In a month-long study in rats, sesame oil supplementation protected against damage to heart cells.
In the same experiment, antioxidant activity rose in rats given roughly 2 or 5 ml of sesame oil per pound (5 or 10 ml per kg) of body weight daily.
Topical use of sesame oil may yield similar antioxidant benefits. A rat study indicated it could reduce cell damage by inhibiting enzymes like xanthine oxidase and molecules such as nitric oxide that generate free radicals.
Summary Sesame oil is rich in
antioxidants that may offer meaningful health benefits.
2. Strong anti-inflammatory effects
Persistent inflammation can be detrimental and contribute to disease, so minimizing it is important.
In traditional Taiwanese medicine, sesame oil has long been used for its anti-inflammatory actions to treat joint inflammation, toothaches, and minor wounds.
More recent laboratory and animal research indicates sesame oil can lower inflammation, which may be one of its primary health-promoting actions.
For instance, in vitro studies have shown sesame oil reduces inflammatory markers like nitric oxide production.
Still, human trials are necessary to confirm these findings.
Summary Animal and lab studies suggest sesame oil may reduce inflammation, but more research in humans is required.
3. Beneficial for heart health
Extensive research supports that diets rich in unsaturated fats promote heart health (9, ).
Sesame oil is composed of about 82% unsaturated fatty acids.
It is particularly high in omega-6 fatty acids, a type of polyunsaturated fat that’s essential in the diet and plays a role in preventing heart disease.
Animal studies suggest sesame oil may guard against heart disease and slow plaque buildup in arteries.
When used instead of oils high in saturated fat, sesame oil may also lower cholesterol.
In a one-month trial with 48 adults, those who consumed 4 tablespoons (59 ml) of sesame oil daily experienced larger decreases in LDL (bad) cholesterol and triglycerides than participants who consumed olive oil.
Summary Sesame oil is a heart-healthy oil rich in unsaturated fats that may lower risk factors for cardiovascular disease.
4. May help manage blood sugar
Sesame oil may aid in maintaining healthy blood sugar levels, which is especially important for people with diabetes.
One study found that diabetic rats fed a diet containing 6% sesame oil for 42 days had significant reductions in blood glucose compared with rats not receiving the oil.
Sesame oil might also influence long-term blood sugar control.
In a study of 46 adults with type 2 diabetes, taking sesame oil for 90 days significantly lowered fasting blood glucose and hemoglobin A1c (HbA1c) compared with a placebo group. HbA1c reflects long-term blood sugar control.
Summary Consuming sesame oil may help regulate blood sugar, particularly for individuals with diabetes.
5. Potential to ease arthritis
Osteoarthritis affects almost 15% of people and is a frequent source of joint pain.
Multiple rodent studies have associated sesame oil with improvements in arthritis.
In a 28-day experiment, rats given daily doses of 0.5 ml per pound (1 ml per kg) of body weight showed reduced oxidative stress markers and fewer arthritic symptoms, such as joint pain.
Although animal research indicates sesame oil may relieve arthritis symptoms, human studies are still needed.
Summary Sesame oil may reduce arthritis symptoms, but current evidence comes mainly from animal studies.
6. May aid wound and burn healing
Besides being consumed, sesame oil can be applied topically to treat wounds and burns.
Ozone is a naturally occurring gas used clinically since 1914 to treat infections. Oils infused with ozone — called ozonated oils — are applied topically for various skin conditions.
In one rat study, applying ozonated sesame oil increased collagen levels in wound tissue. Collagen is crucial for wound repair.
Other animal studies have reported that sesame oil reduced healing time for burns and wounds in mice, though human data are lacking (, 23).
The oil’s ability to accelerate wound and burn healing likely stems from its antioxidant and anti-inflammatory actions.
Summary Sesame oil may promote healing of wounds and burns, but current evidence is limited to animal research.
7. May offer some UV protection
Research indicates sesame oil might shield skin from UV-induced damage, likely because of its antioxidant content.
It’s reported to block about 30% of UV rays, whereas many other oils like coconut, peanut, and olive block roughly 20%.
Although some sources describe sesame oil as a natural sunscreen with inherent SPF, evidence about its effectiveness against strong sun exposure is limited. Therefore, it’s advisable to use conventional sunscreen.
Summary Sesame oil may provide modest UV protection, but evidence is limited; sunscreen is still recommended.
8–10. Other possible benefits
While evidence is limited, some studies suggest sesame oil may offer additional benefits:
- May enhance sleep quality. One study found that applying sesame oil to the forehead of 20 participants during seven 30-minute sessions over two weeks improved sleep quality and overall quality of life versus a placebo.
- Topical use may reduce pain. Some studies indicate that massaging with sesame oil can alleviate arm and leg pain.
- May improve hair condition. Compounds in sesame oil may boost hair shine and strength. An eight-week trial showed that daily supplements containing sesamin and vitamin E improved hair strength and shine.
Summary Though more research is necessary, sesame oil may help with sleep, relieve pain when used topically, and support hair health.
Simple ways to incorporate it into meals
Sesame oil adds a toasty, nutty note to many dishes and is a staple in Asian and Middle Eastern cooking.
Different forms of sesame oil offer distinct flavors and uses.
Unrefined sesame oil is light in color with a nutty taste and is best for low- to medium-heat cooking. Refined sesame oil is more processed, has a neutral flavor, and suits high-heat methods like deep- or stir-frying.
Toasted sesame oil is dark brown with a rich aroma, making it ideal for dressings and marinades.
Here are easy ways to add sesame oil to your diet:
- stir-fries
- sesame noodle dishes
- marinades for meats or fish
- vinaigrettes
- sauces and dips
You can find sesame oil at many grocery stores or buy it online.
Summary Sesame oil is versatile in cooking, and different varieties suit different culinary needs.
The bottom line
Sesame oil is a tasty, healthful fat to include in your diet.
Owing to its antioxidants and anti-inflammatory properties, it may benefit the heart, joints, skin, hair, and more. Still, further human research is needed to fully establish these benefits.
To potentially reap the advantages of sesame oil, incorporate it into recipes and enjoy it as part of a balanced diet.























Leave a Reply
You must be logged in to post a comment.